Expo
Medica
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

- Cranial Accelerometry Headset Enables Timely and Accurate Prehospital Detection of LVO Strokes
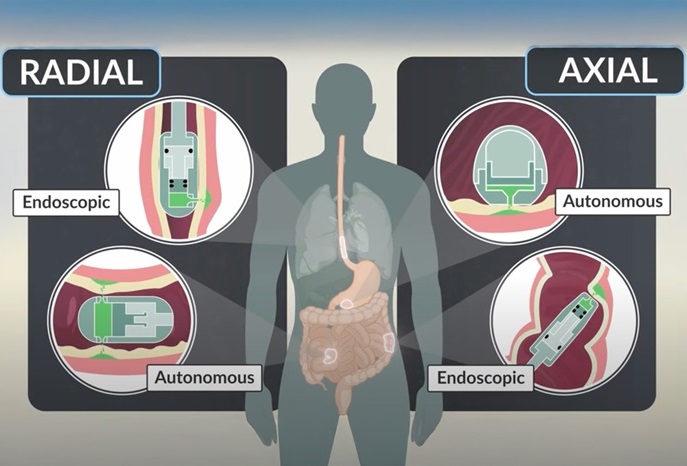
- Ingestible Capsule Pump Drugs Directly into Walls of GI Tract
- New Tool Improves Liver Cancer Detection
- New Antibody Could Be Promising Cancer Treatment
- Cutting-Edge Monitoring Device Could Outsmart Superbugs Resistant to Antibiotics
- Novel Neural Interface to Help Diagnose and Treat Neurological Disorders with Minimal Surgical Risks
- New Lens System for Endoscopes Offers Physicians Unprecedented View of Inside the Body
- Wireless, Fully Implantable LVAD System to Make Life Easier for Heart Failure Patients
- Newly Developed Coating Makes Medical Devices Clot-Free
- New Research Helps Choose Most Ideal Hip Implant for Replacement Surgery
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Start-Ups To Once Again Play Starring Role at MEDICA 2024
- Boston Scientific to Acquire AFib Ablation Company Cortex
- Hologic Acquires Gynesonics to Strengthen Existing Gynecological Surgical Business
- Smith+Nephew and JointVue Partner on Ultrasound Preoperative Planning in Robotics-Assisted Surgery
- Stryker Completes Acquisition of NICO Corporation
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
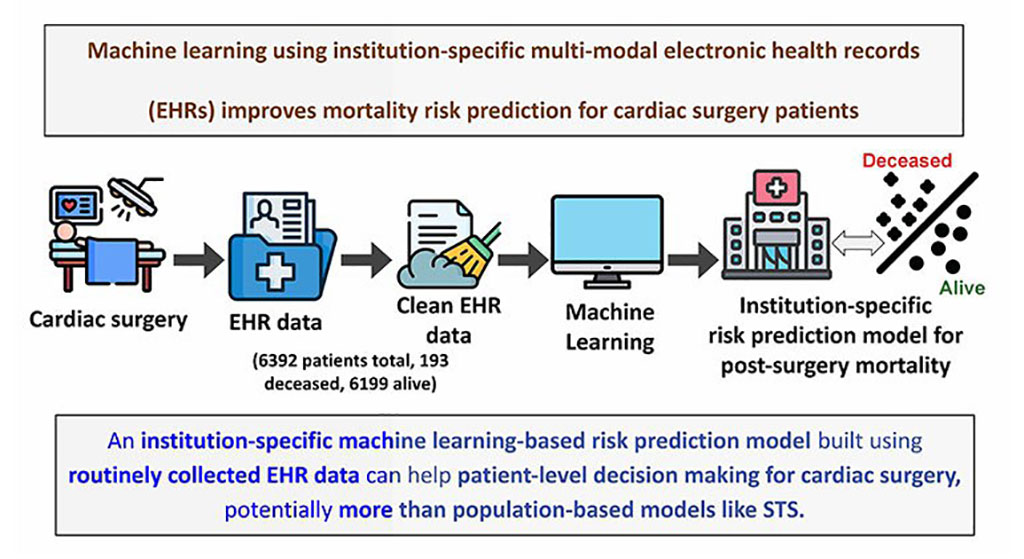
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds

Expo
 Medica
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
Medica
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us

 Medica
Medica
- Cranial Accelerometry Headset Enables Timely and Accurate Prehospital Detection of LVO Strokes
- Ingestible Capsule Pump Drugs Directly into Walls of GI Tract
- New Tool Improves Liver Cancer Detection
- New Antibody Could Be Promising Cancer Treatment
- Cutting-Edge Monitoring Device Could Outsmart Superbugs Resistant to Antibiotics
- Novel Neural Interface to Help Diagnose and Treat Neurological Disorders with Minimal Surgical Risks
- New Lens System for Endoscopes Offers Physicians Unprecedented View of Inside the Body
- Wireless, Fully Implantable LVAD System to Make Life Easier for Heart Failure Patients
- Newly Developed Coating Makes Medical Devices Clot-Free
- New Research Helps Choose Most Ideal Hip Implant for Replacement Surgery
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Start-Ups To Once Again Play Starring Role at MEDICA 2024
- Boston Scientific to Acquire AFib Ablation Company Cortex
- Hologic Acquires Gynesonics to Strengthen Existing Gynecological Surgical Business
- Smith+Nephew and JointVue Partner on Ultrasound Preoperative Planning in Robotics-Assisted Surgery
- Stryker Completes Acquisition of NICO Corporation
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- Richard Wolf to Present Innovative System Solutions at Germany Trade Show
- PROTEC to Launch New Motorized PRS 500 B X-ray System
- Randox to Showcase Future-Proofing Diagnostic Technology at Trade Fair
- NDS Announces New OR Networking Solution at Germany Trade Show
- Global Good and Motic Announce AI-Powered Microscope at MEDICA 2017
- Rober Showcases Pioneering ‘Zero Pressure’ Mattresses in Germany
- UK Companies Showcase Life-Saving Solutions at Medica 2018
- Siemens Healthineers Showcases ACUSON Ultrasound Product Portfolio
- Metaltronica Presents Digital Mammography Systems at Medical Trade Fair
- Canon Displays New Products at MEDICA Show
- Samsung Medison Exhibits New HERA I10 Combination Ultrasound System
- Medtronic Displays Patient Monitoring Systems at MEDICA 2019
- Healcerion Exhibits SONON Wireless Handheld Ultrasound at MEDICA 2019
- Hans Rudolph Exhibits Latest Range of Oro-Nasal Masks at MEDICA 2019
- EIZO Demonstrates CuratOR Alipe IP-Based Video Management Solution at MEDICA 2019
- Fisher & Paykel Demonstrates Humidified Nasal High Flow System for Delivering Respiratory Support at MEDICA 2021
- Axcent Medical Showcases Premium ICU Ventilator and Electronic Anesthesia Workstation at MEDICA 2021
- MESI Demonstrates Revolutionary mTABLET System at MEDICA 2021
- Microlife Presents the Only Blood Pressure Monitor with Integrated AFIB Detection at MEDICA 2021
- Innovative Health Presents Its Breakthrough Versatile and Low Cost Non-Electric Infusion System at MEDICA 2021
- Huntleigh Exhibits Range of Vital Signs Monitoring Solutions at MEDICA 2022
- Owen Mumford Presents Cutting-Edge Capillary Blood Sampling Devices for POC Testing
- Noul Demonstrates AI-Driven On-Site Diagnostics Platform at MEDICA 2022
- KUKA Presents Robot-Based Assistance Systems at MEDICA 2022
- Heyer Medical Exhibits State-Of-The-Art Ventilators, Anesthesia Workstations and Surgical Lights
- LG Electronics Exhibits High Resolution Monitors for Surgery and Medical Diagnosis
- Advantech Demonstrates High-Performance Healthcare Systems and Solutions
- MAVIG Highlights X-Ray Protective Clothing and Suspension Systems for Medical Equipment
- EIZO GmbH Presents New 4K Visualization Solutions for Operating Room
- OptoMedic Showcases World of Fluorescence Endoscopy Technologies
- Norav Medical Demonstrates Advanced ECG Solutions
- MAVIG Highlights Latest Innovations in X-Ray Protection and Medical Suspension Systems
- EndoSemio Features Wireless Endoscope Tracheostomy Kit for Advanced Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Brain Navi Demonstrates First Autonomous Surgical Navigation Robot for Neurosurgery