Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

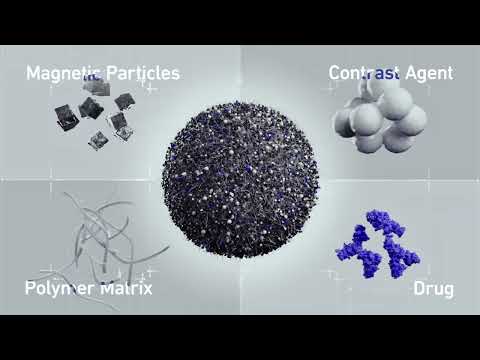
- Nanohydrogels Guide Medicine to Tumors Without Damaging Healthy Tissue
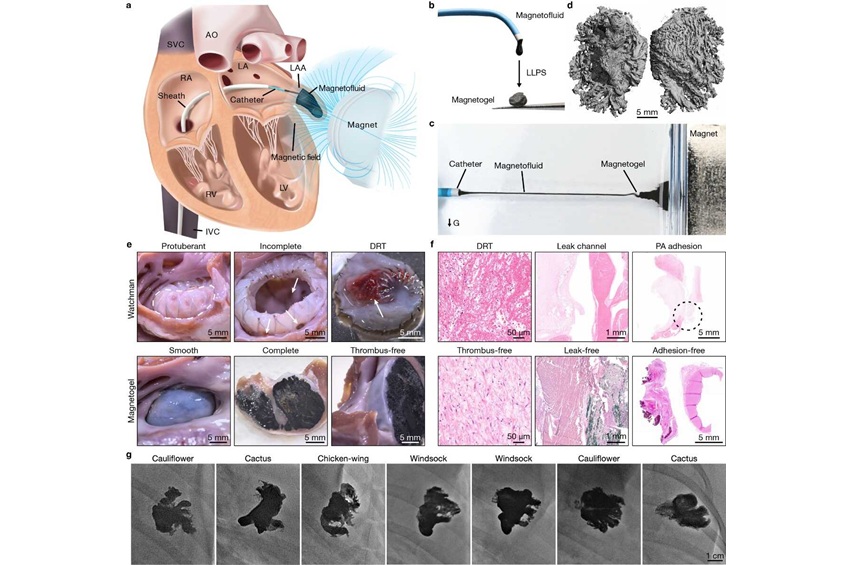
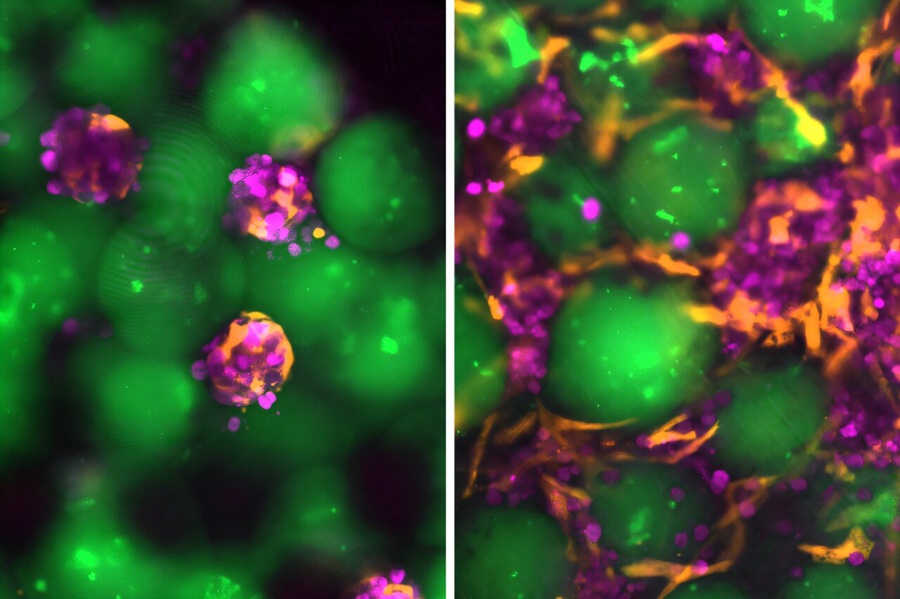
- Magnetic Gel Offers Safer and More Effective Atrial Fibrillation Treatment
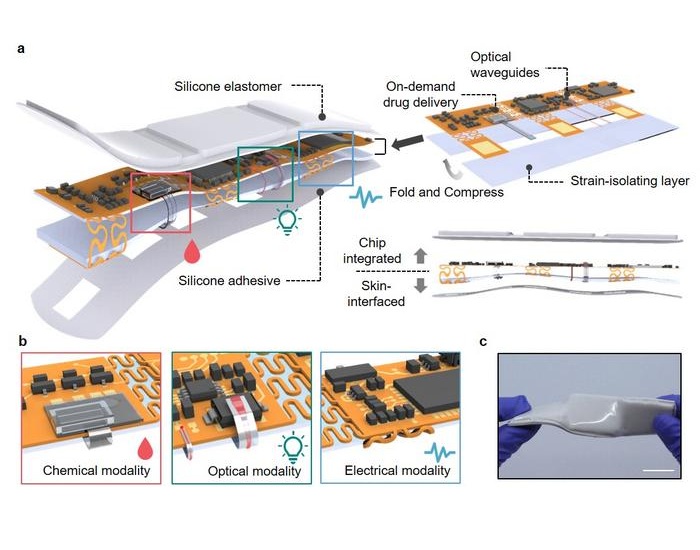
- Hydrogel Biosensor Detects and Differentiates Blood Circulation Complications
- Spray-Type Technology Coats Transplant Organs with Immunosuppressants to Prevent Rejection
- Machine-Learning Model Predicts Preeclampsia in Late Pregnancy
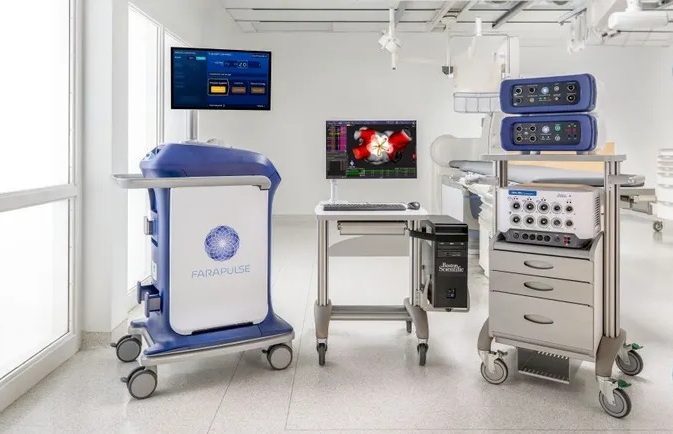
- Pulsed Field Ablation Technology Cleared in Europe for Persistent AFib
- AI-Powered Imaging Brings Real-Time Margin Clarity to Breast Cancer Surgery
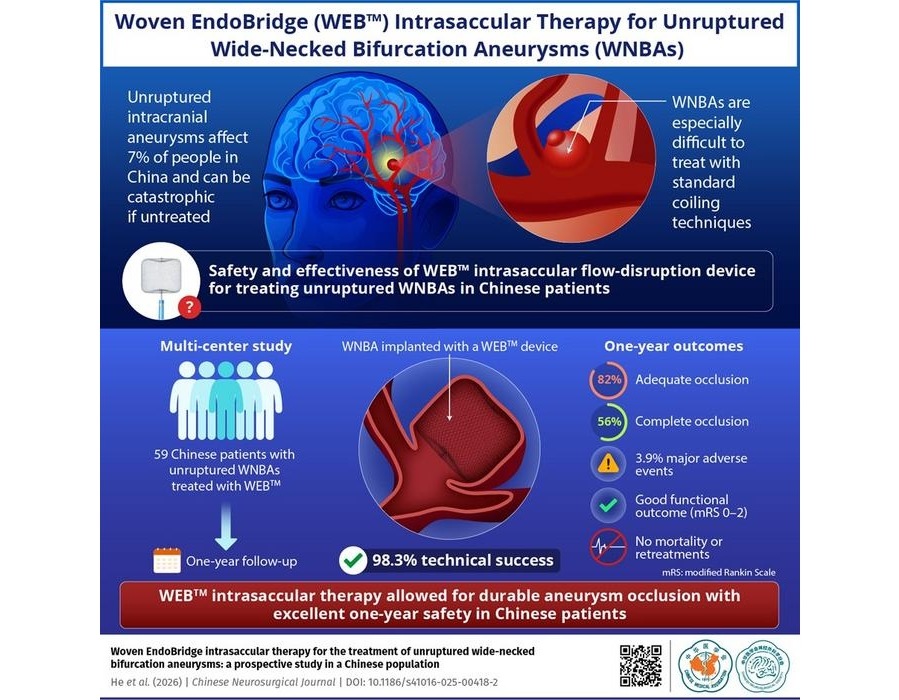
- Minimally Invasive Device Safely Treats Challenging Brain Aneurysms
- Surgical Robot Makes Complex Liver Tumor Surgery Safer and Less Invasive
- Fluorescence Probe Paired with Engineered Enzymes Lights Up Tumors for Easier Surgical Removal
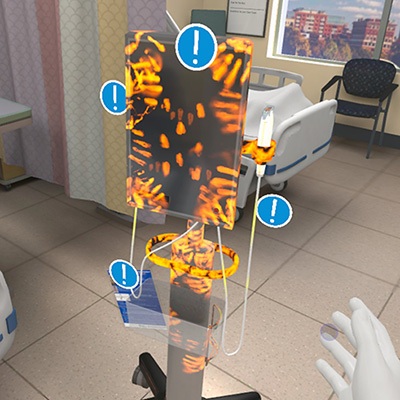
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Medtronic to Acquire Coronary Artery Medtech Company CathWorks
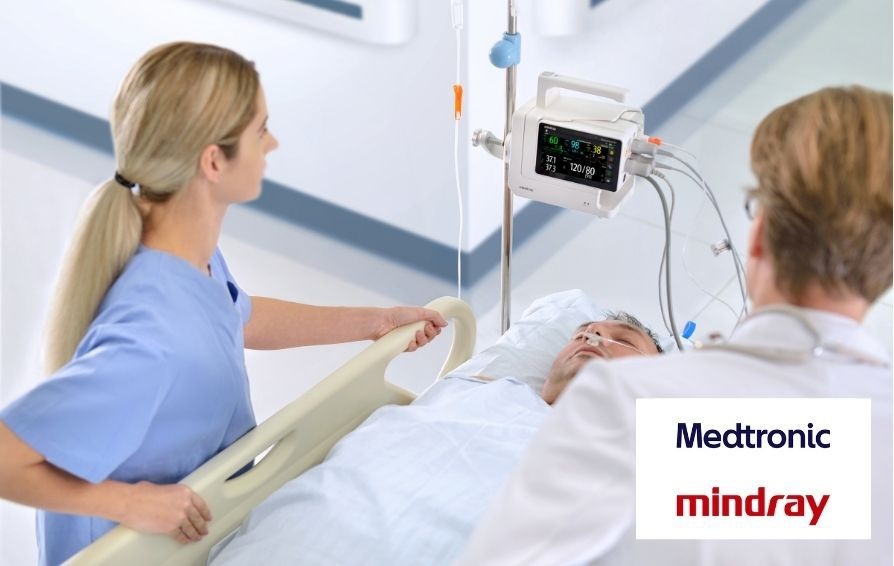
- Medtronic and Mindray Expand Strategic Partnership to Ambulatory Surgery Centers in the U.S.
- FDA Clearance Expands Robotic Options for Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to debut specialised Biotech & Life Sciences Zone as sector growth accelerates globally
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to bring together key UAE government entities during the groundbreaking 2026 edition

 Expo
Expo
- Nanohydrogels Guide Medicine to Tumors Without Damaging Healthy Tissue
- Magnetic Gel Offers Safer and More Effective Atrial Fibrillation Treatment
- Hydrogel Biosensor Detects and Differentiates Blood Circulation Complications
- Spray-Type Technology Coats Transplant Organs with Immunosuppressants to Prevent Rejection
- Machine-Learning Model Predicts Preeclampsia in Late Pregnancy
- Pulsed Field Ablation Technology Cleared in Europe for Persistent AFib
- AI-Powered Imaging Brings Real-Time Margin Clarity to Breast Cancer Surgery
- Minimally Invasive Device Safely Treats Challenging Brain Aneurysms
- Surgical Robot Makes Complex Liver Tumor Surgery Safer and Less Invasive
- Fluorescence Probe Paired with Engineered Enzymes Lights Up Tumors for Easier Surgical Removal
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Medtronic to Acquire Coronary Artery Medtech Company CathWorks
- Medtronic and Mindray Expand Strategic Partnership to Ambulatory Surgery Centers in the U.S.
- FDA Clearance Expands Robotic Options for Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to debut specialised Biotech & Life Sciences Zone as sector growth accelerates globally
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to bring together key UAE government entities during the groundbreaking 2026 edition