Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

- Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment Reduces Tumor Size, Improves Surgical Removal
- Light-Activated Ink Repairs Heart by Non-Invasively Manipulating Cardiac Tissue Activity
- New Epilepsy Tool Cuts Misdiagnoses by 70% Using Routine EEGs
- AI-Powered Prediction Model Enhances Blood Transfusion Decision-Making in ICU Patients
- Wearable Devices Detect and Predict Inflammatory Bowel Disease Flare-Ups
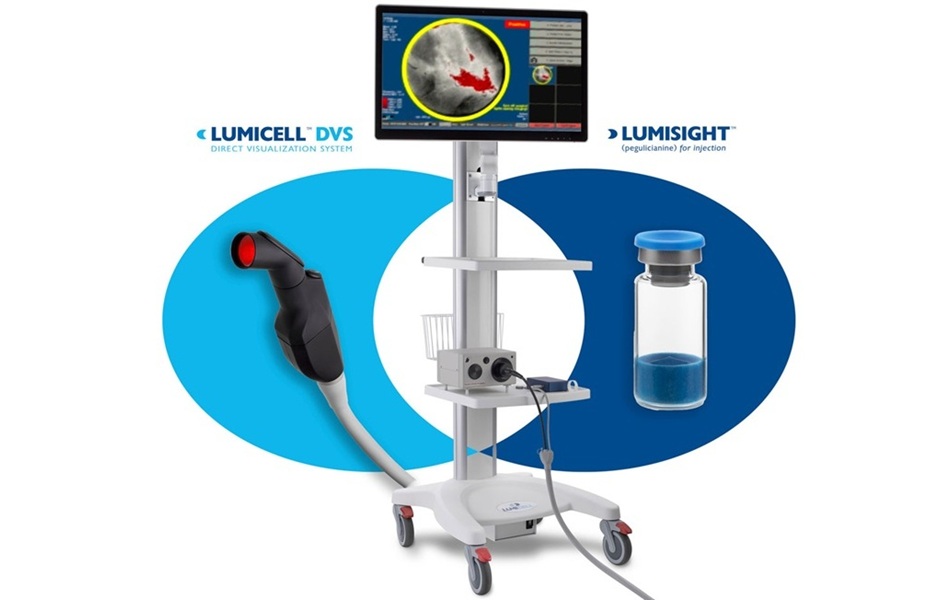
- Pioneering Technology Enables Real-Time Detection of Residual Breast Cancer During Lumpectomy
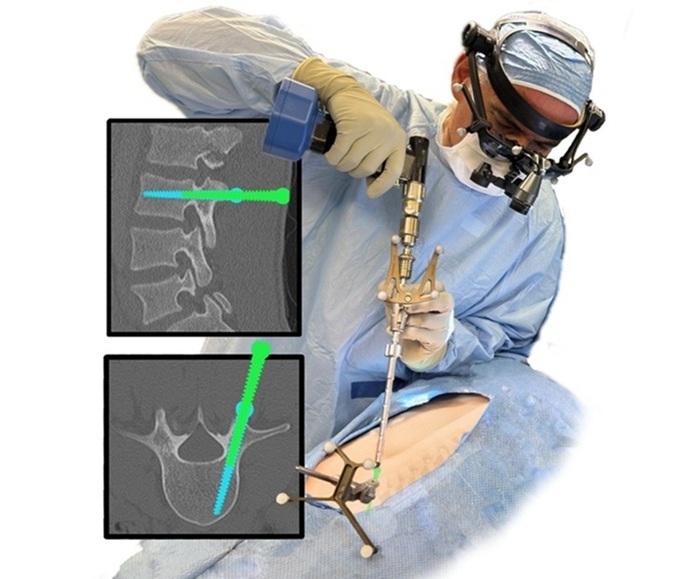
- Advanced Augmented Reality System to Transform Spine Surgery
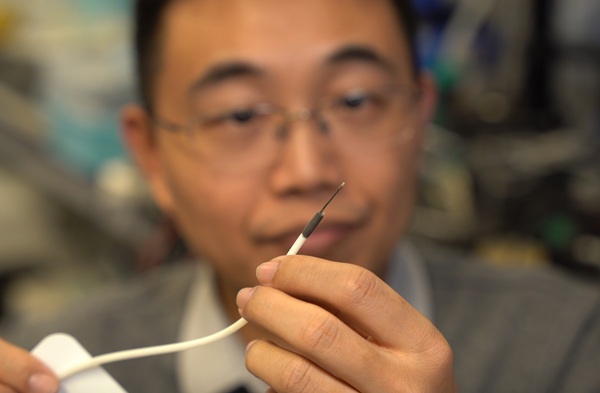
- World's Smallest Multifunctional Biomedical Robot Holds Promise for Interventional Diagnosis and Treatment
- New Imaging Technique a Game-Changer for Bladder Cancer Surgery
- Synthetic Material for Use in Spinal Surgery to Revolutionize Bone Graft Technology
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company Intera Oncology
- MEDICA 2024 to Highlight Hot Topics of MedTech Industry
- Start-Ups To Once Again Play Starring Role at MEDICA 2024
- Boston Scientific to Acquire AFib Ablation Company Cortex
- Hologic Acquires Gynesonics to Strengthen Existing Gynecological Surgical Business
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
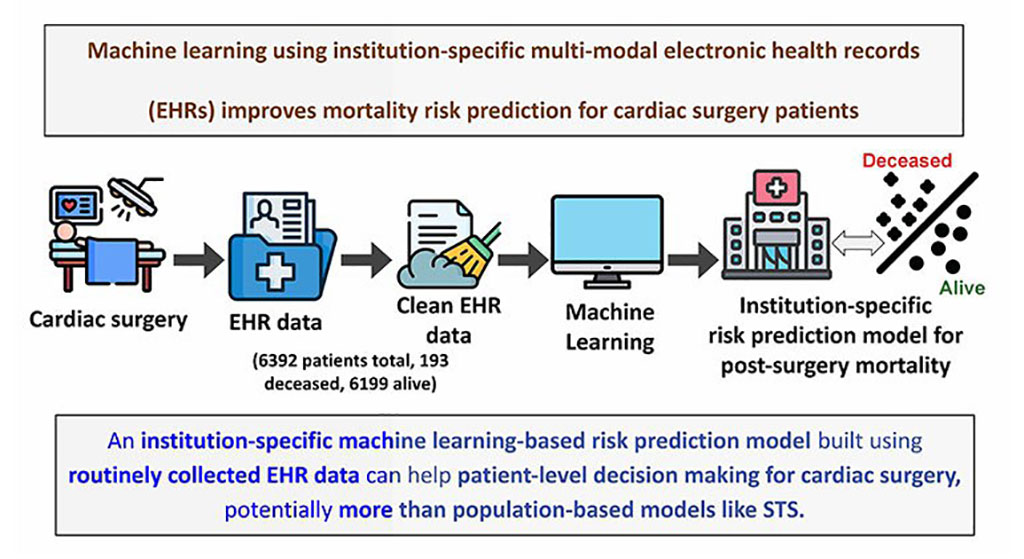
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment Reduces Tumor Size, Improves Surgical Removal
- Light-Activated Ink Repairs Heart by Non-Invasively Manipulating Cardiac Tissue Activity
- New Epilepsy Tool Cuts Misdiagnoses by 70% Using Routine EEGs
- AI-Powered Prediction Model Enhances Blood Transfusion Decision-Making in ICU Patients
- Wearable Devices Detect and Predict Inflammatory Bowel Disease Flare-Ups
- Pioneering Technology Enables Real-Time Detection of Residual Breast Cancer During Lumpectomy
- Advanced Augmented Reality System to Transform Spine Surgery
- World's Smallest Multifunctional Biomedical Robot Holds Promise for Interventional Diagnosis and Treatment
- New Imaging Technique a Game-Changer for Bladder Cancer Surgery
- Synthetic Material for Use in Spinal Surgery to Revolutionize Bone Graft Technology
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company Intera Oncology
- MEDICA 2024 to Highlight Hot Topics of MedTech Industry
- Start-Ups To Once Again Play Starring Role at MEDICA 2024
- Boston Scientific to Acquire AFib Ablation Company Cortex
- Hologic Acquires Gynesonics to Strengthen Existing Gynecological Surgical Business
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds