Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

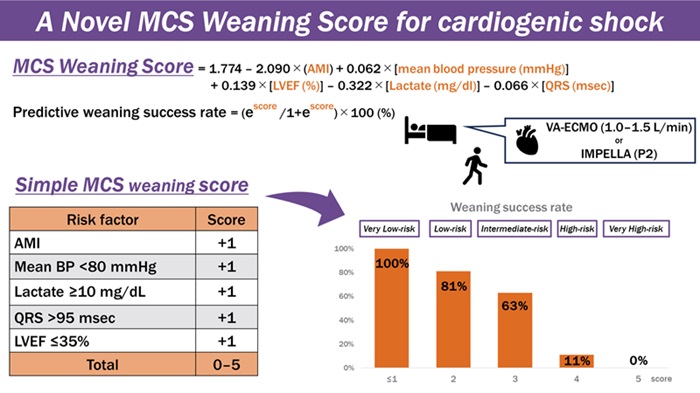
- Simple Risk Score Model Helps Wean Patients from Mechanical Circulatory Support
- Re-Engineered Immune Cells Penetrate and Kill Solid Tumors
- New Nanoparticle Nanotherapy Infusion Cleans Arteries
- Fluorescence Imaging a Game-Changer for Bedside Biofilm Detection
- Spongelike Bandage with Antimicrobial Efficacy Stops Hemorrhaging and Mitigates Risk of Infection
- Portable Surgical Robot Seamlessly Integrates into Any OR for Performing Cholecystectomy Procedures
- New Thoracic Surgery Risk Calculators Support Preoperative Decision-Making
- Surgical Platform with Miniature Humanoid-Shaped Robotic Arms Provides Human Level Dexterity
- Precision Surgical Technique Enables Lymph Node Detection and Removal in Endometrial Cancer
- Glowing Approach Helps Surgeons Assess Neural Blood Flow in Chronic Nerve Compression Neuropathy
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
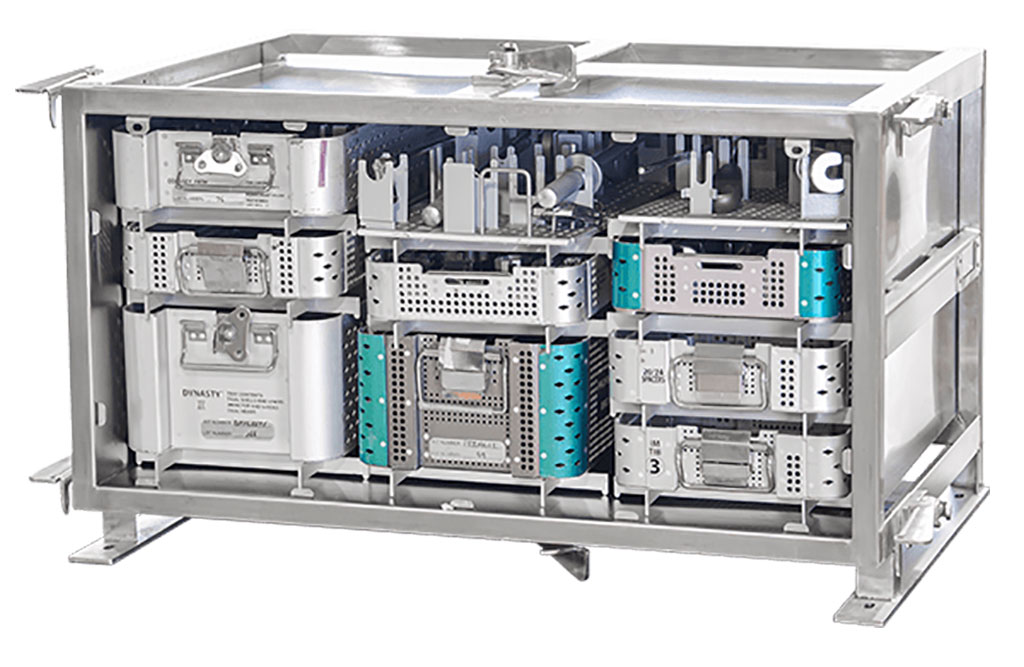
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Smith+Nephew and JointVue Partner on Ultrasound Preoperative Planning in Robotics-Assisted Surgery
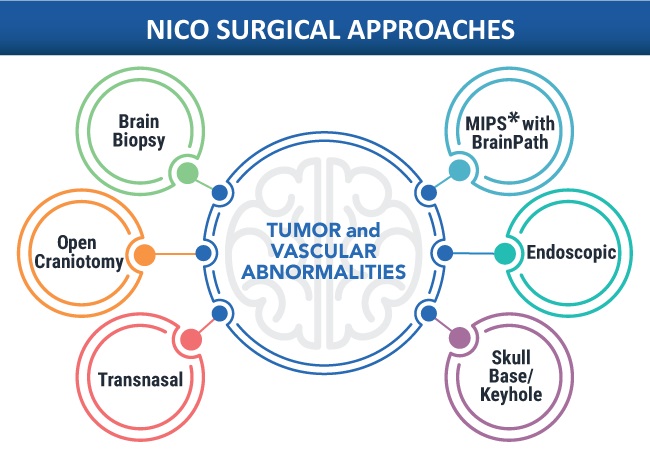
- Stryker Completes Acquisition of NICO Corporation
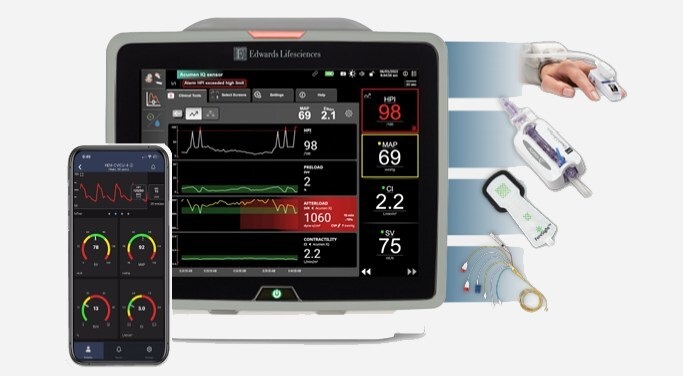
- BD Completes Acquisition of Critical Care from Edwards Lifesciences
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
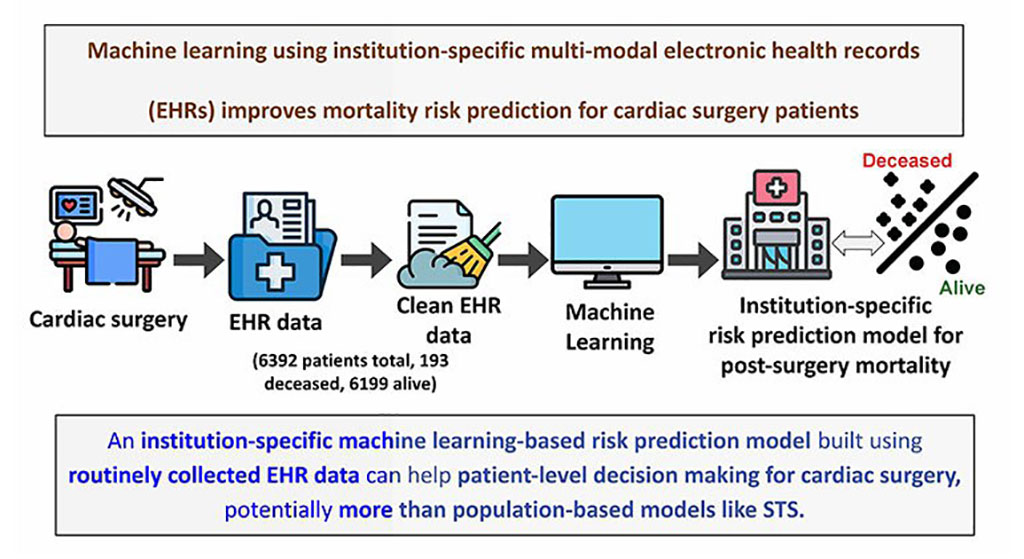
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
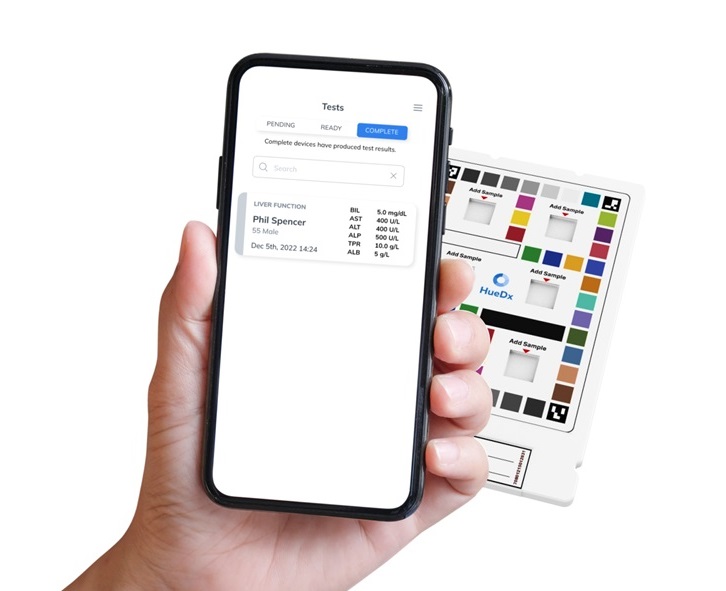
- Smartphone-Enabled, Paper-Based Quantitative Diagnostic Platform Transforms POC Testing
- New 8-Minute Blood Test to Diagnose or Rule Out Heart Attack Shortens ED Stay
- 5-Minute Multiplex PCR Testing System to Redefine Point-Of-Care Diagnostics
- POCT for Infectious Diseases Delivers Laboratory Equivalent Pathology Results
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- Simple Risk Score Model Helps Wean Patients from Mechanical Circulatory Support
- Re-Engineered Immune Cells Penetrate and Kill Solid Tumors
- New Nanoparticle Nanotherapy Infusion Cleans Arteries
- Fluorescence Imaging a Game-Changer for Bedside Biofilm Detection
- Spongelike Bandage with Antimicrobial Efficacy Stops Hemorrhaging and Mitigates Risk of Infection
- Portable Surgical Robot Seamlessly Integrates into Any OR for Performing Cholecystectomy Procedures
- New Thoracic Surgery Risk Calculators Support Preoperative Decision-Making
- Surgical Platform with Miniature Humanoid-Shaped Robotic Arms Provides Human Level Dexterity
- Precision Surgical Technique Enables Lymph Node Detection and Removal in Endometrial Cancer
- Glowing Approach Helps Surgeons Assess Neural Blood Flow in Chronic Nerve Compression Neuropathy
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Smith+Nephew and JointVue Partner on Ultrasound Preoperative Planning in Robotics-Assisted Surgery
- Stryker Completes Acquisition of NICO Corporation
- BD Completes Acquisition of Critical Care from Edwards Lifesciences
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- Smartphone-Enabled, Paper-Based Quantitative Diagnostic Platform Transforms POC Testing
- New 8-Minute Blood Test to Diagnose or Rule Out Heart Attack Shortens ED Stay
- 5-Minute Multiplex PCR Testing System to Redefine Point-Of-Care Diagnostics
- POCT for Infectious Diseases Delivers Laboratory Equivalent Pathology Results
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing


















_2.jpeg)