Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

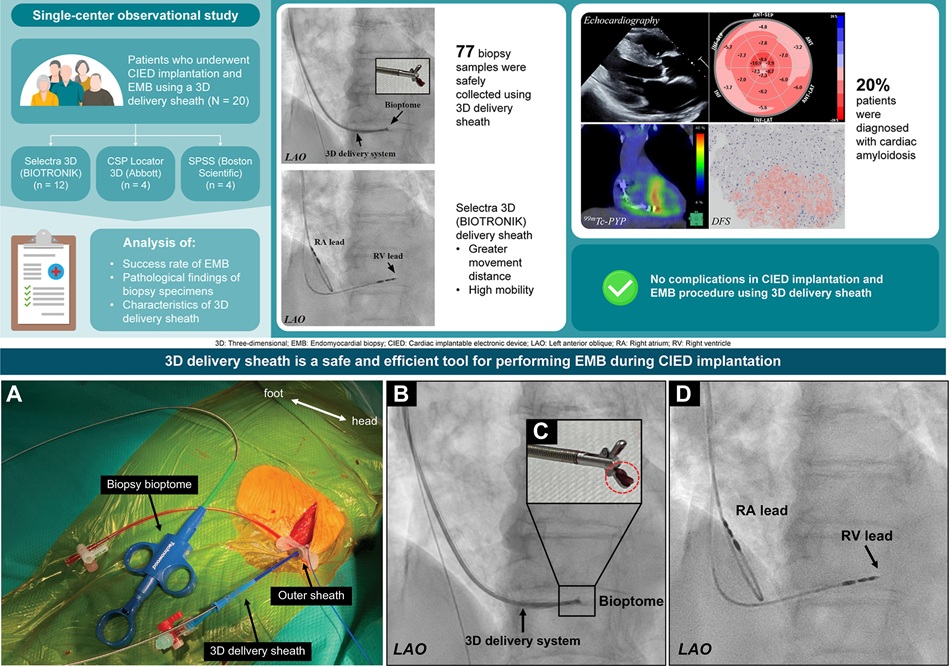
- AI Outperforms Humans at Analyzing Long-Term ECG Recordings
- Skin Patch Activates New Gene Switch to Treat Diabetes
- Zinc-Based Dissolvable Implants to Transform Bone Repair
- Self-Healing Electronic Skin Repairs Itself in Seconds After Damage
- Light-Activated ‘Smart Bomb’ Advances Breast Cancer Treatment
- New Surface Coating Could Prevent Blood Clotting in Medical Devices and Implants
- Dumbbell-Shaped Thrombectomy Device Offers Novel Approach to Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Treatment
- Novel Catheter Mimics Snake Teeth to Grab Blood Clots
- New Laparoscopic Imaging Technique Accurately Maps Biological Tissue for Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Mechanical Heart Valve Replacements Have Better Long-Term Survival, Study Finds
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Smartwatches Could Detect Congestive Heart Failure
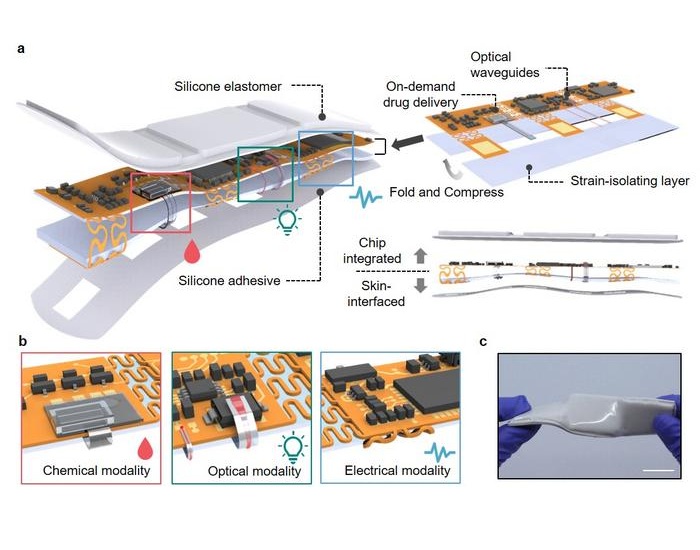
- Versatile Smart Patch Combines Health Monitoring and Drug Delivery
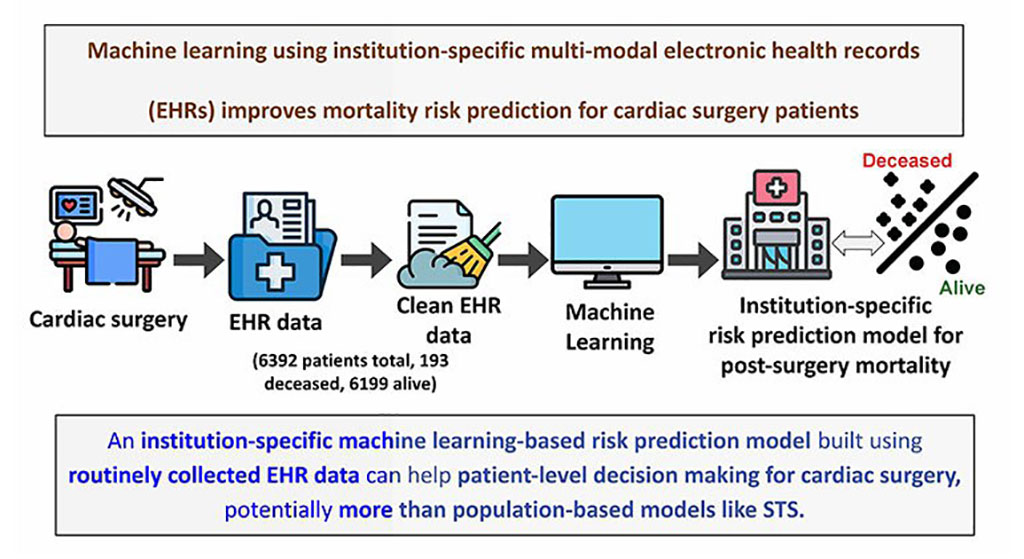
- Machine Learning Model Improves Mortality Risk Prediction for Cardiac Surgery Patients
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- AI Outperforms Humans at Analyzing Long-Term ECG Recordings
- Skin Patch Activates New Gene Switch to Treat Diabetes
- Zinc-Based Dissolvable Implants to Transform Bone Repair
- Self-Healing Electronic Skin Repairs Itself in Seconds After Damage
- Light-Activated ‘Smart Bomb’ Advances Breast Cancer Treatment
- New Surface Coating Could Prevent Blood Clotting in Medical Devices and Implants
- Dumbbell-Shaped Thrombectomy Device Offers Novel Approach to Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Treatment
- Novel Catheter Mimics Snake Teeth to Grab Blood Clots
- New Laparoscopic Imaging Technique Accurately Maps Biological Tissue for Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Mechanical Heart Valve Replacements Have Better Long-Term Survival, Study Finds
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Smartwatches Could Detect Congestive Heart Failure
- Versatile Smart Patch Combines Health Monitoring and Drug Delivery
- Machine Learning Model Improves Mortality Risk Prediction for Cardiac Surgery Patients
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity