Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient Care
Point of CareBusiness
Events

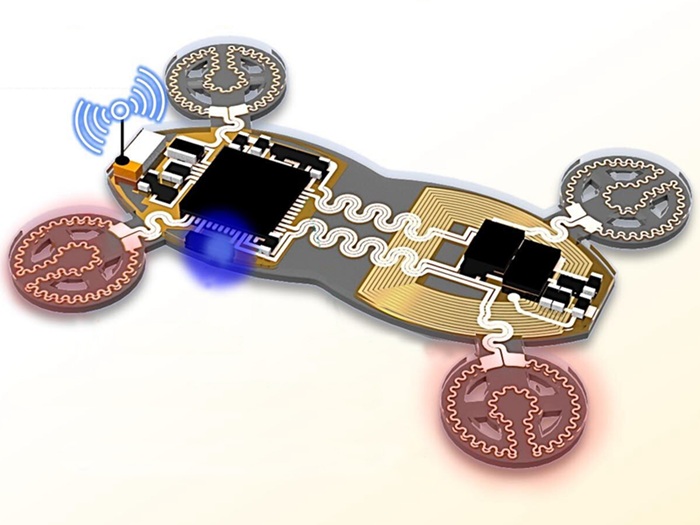
- Flexible Semi-Autonomous Robot Could Deliver Medicine Inside Body
- Handheld Device Could Transform Heart Disease Screening
- Gene Discovery Could Help Grow New Heart Arteries
- Neurorestorative Treatment Strategies Hold Promise for Most Severe Forms of Epilepsy
- Study Discovers Invisible Transmission of Common Hospital-Associated Infection
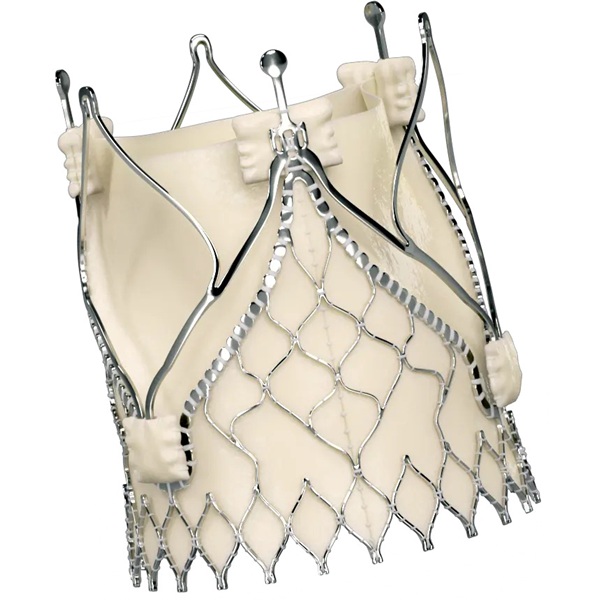
- New Transcatheter Valve Found Safe and Effective for Treating Aortic Regurgitation
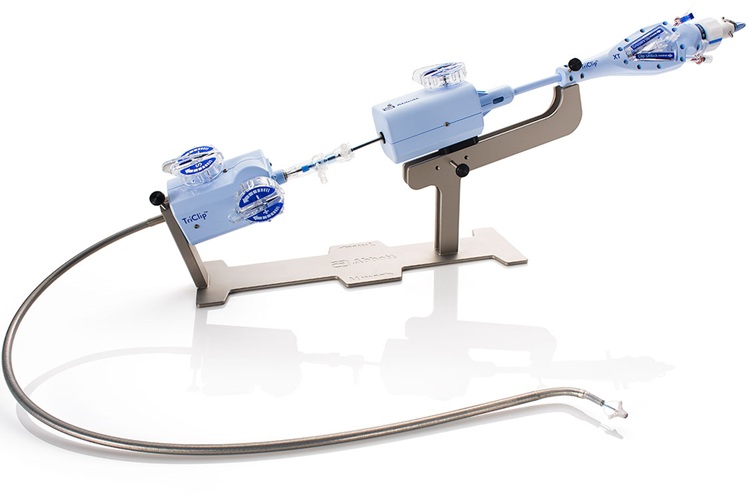
- Minimally Invasive Valve Repair Reduces Hospitalizations in Severe Tricuspid Regurgitation Patients
- Tiny Robotic Tools Powered by Magnetic Fields to Enable Minimally Invasive Brain Surgery
- Magnetic Tweezers Make Robotic Surgery Safer and More Precise
- AI-Powered Surgical Planning Tool Improves Pre-Op Planning
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
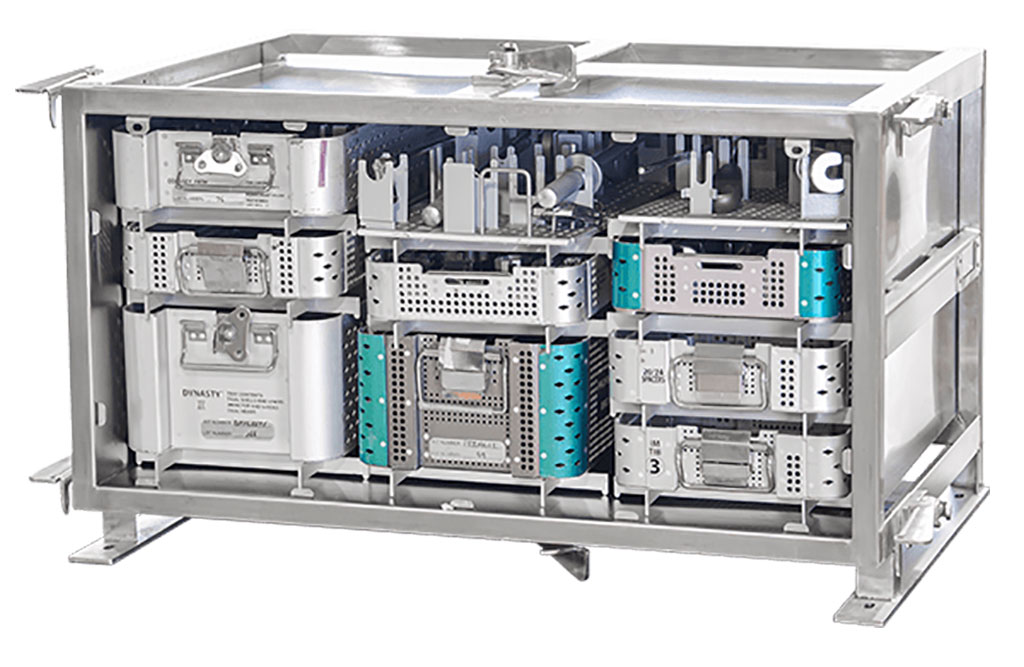
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul
- Teleflex to Acquire BIOTRONIK’s Vascular Intervention Business
- Philips and Mass General Brigham Collaborate on Improving Patient Care with Live AI-Powered Insights
- Smartwatches Could Detect Congestive Heart Failure
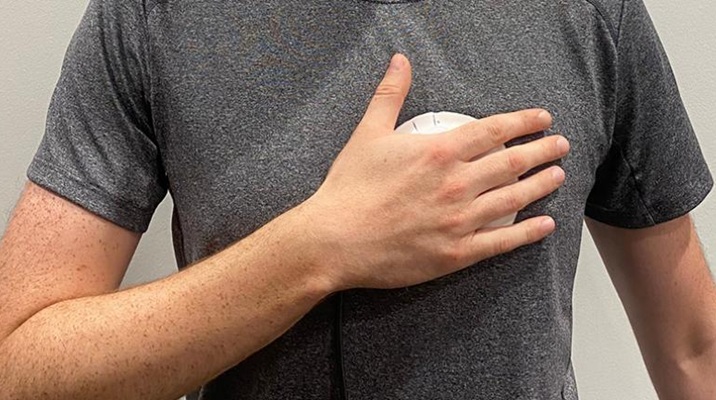
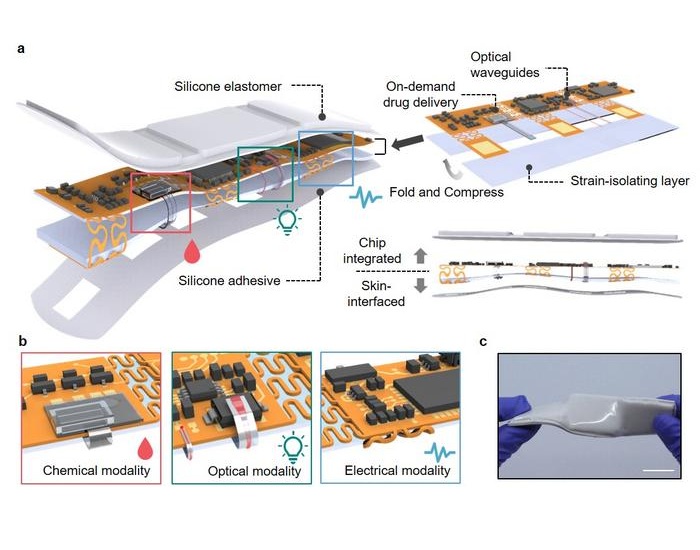
- Versatile Smart Patch Combines Health Monitoring and Drug Delivery
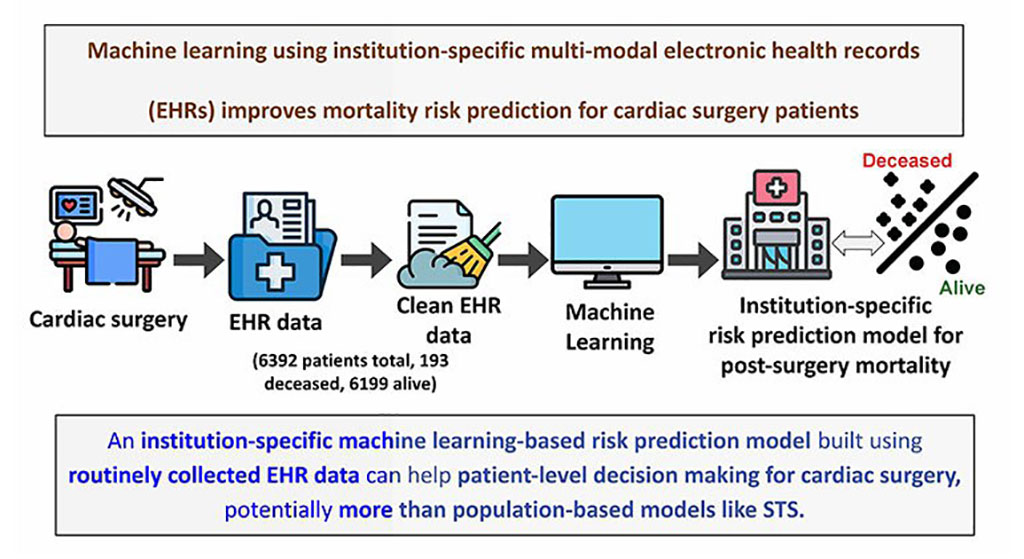
- Machine Learning Model Improves Mortality Risk Prediction for Cardiac Surgery Patients
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity

 Expo
Expo
- Flexible Semi-Autonomous Robot Could Deliver Medicine Inside Body
- Handheld Device Could Transform Heart Disease Screening
- Gene Discovery Could Help Grow New Heart Arteries
- Neurorestorative Treatment Strategies Hold Promise for Most Severe Forms of Epilepsy
- Study Discovers Invisible Transmission of Common Hospital-Associated Infection
- New Transcatheter Valve Found Safe and Effective for Treating Aortic Regurgitation
- Minimally Invasive Valve Repair Reduces Hospitalizations in Severe Tricuspid Regurgitation Patients
- Tiny Robotic Tools Powered by Magnetic Fields to Enable Minimally Invasive Brain Surgery
- Magnetic Tweezers Make Robotic Surgery Safer and More Precise
- AI-Powered Surgical Planning Tool Improves Pre-Op Planning
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul
- Teleflex to Acquire BIOTRONIK’s Vascular Intervention Business
- Philips and Mass General Brigham Collaborate on Improving Patient Care with Live AI-Powered Insights
- Smartwatches Could Detect Congestive Heart Failure
- Versatile Smart Patch Combines Health Monitoring and Drug Delivery
- Machine Learning Model Improves Mortality Risk Prediction for Cardiac Surgery Patients
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity