Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

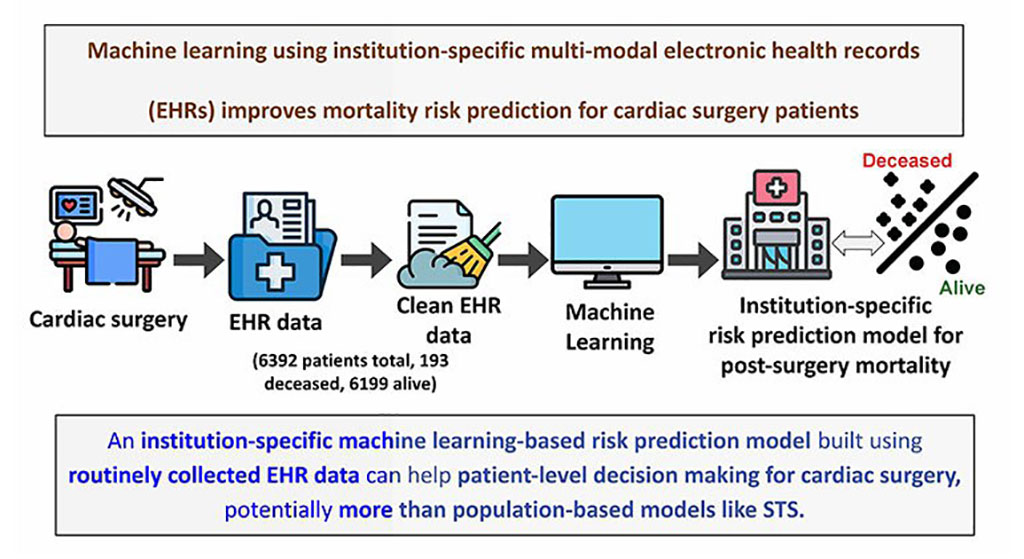
- New Risk Scoring System Considers Role of Chronic Illness in Post-Surgery Mortality
- Implantable Cell-Based Bioelectronic Devices to Enable Patient-Specific Treatment and Disease Monitoring
- Laser-Based Headset Measures Blood Flow to Noninvasively Assess Stroke Risk
- Blocking Activity of Glucagon Hormone Could Treat Common and Challenging Type of Heart Failure
- New Tricuspid Valve Procedure Helps Patients Avoid Open-Heart Surgery
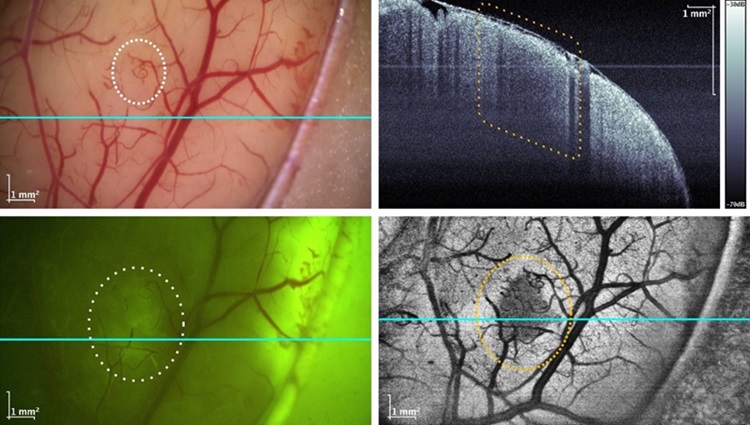
- Fast OCT System Integrated into Neurosurgical Microscope Identifies Tumor Margins During Brain Surgery
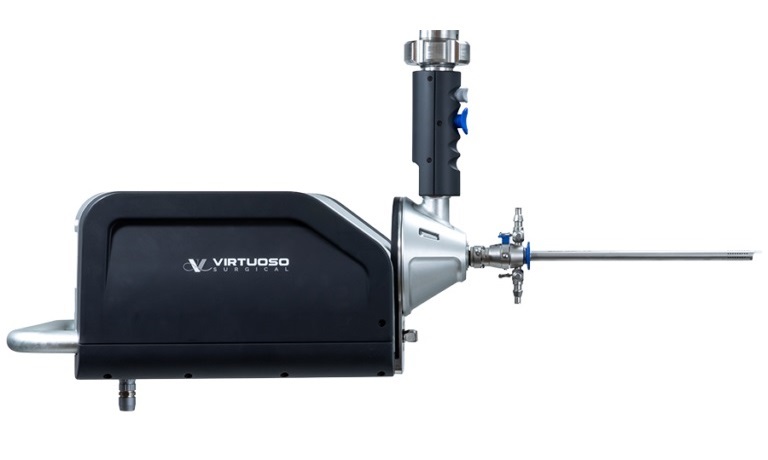
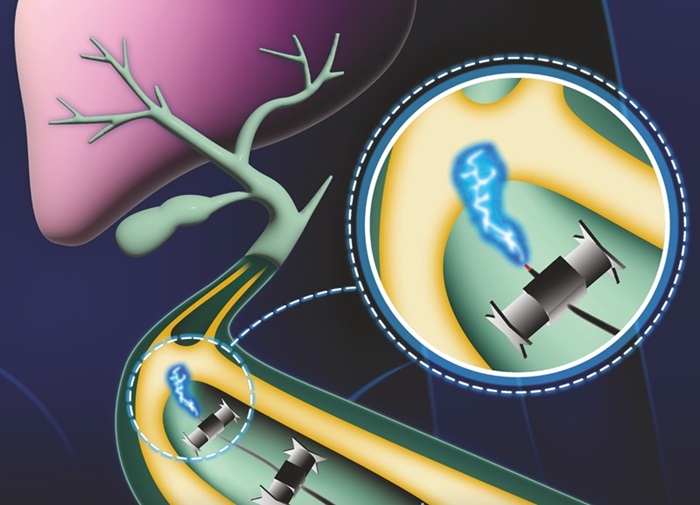
- Miniature Robots Transport Instruments for Endoscopic Microsurgery Through Body
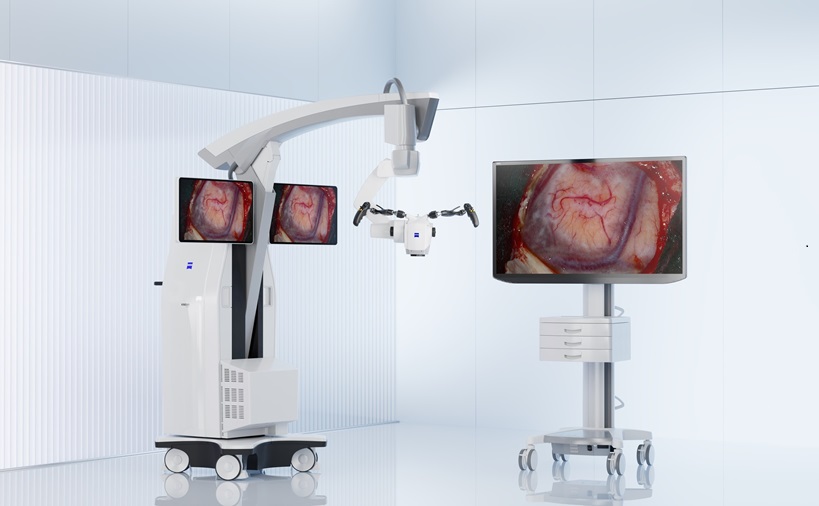
- Robotic Visualization System for Neurosurgery Offers Greater Clarity for Complex Procedures
- Endometrial Ablation for Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Associated with High Risk of Hysterectomy
- Breakthrough Robot Technology Could Allow Entire Surgery to Be Performed Without Human Intervention
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
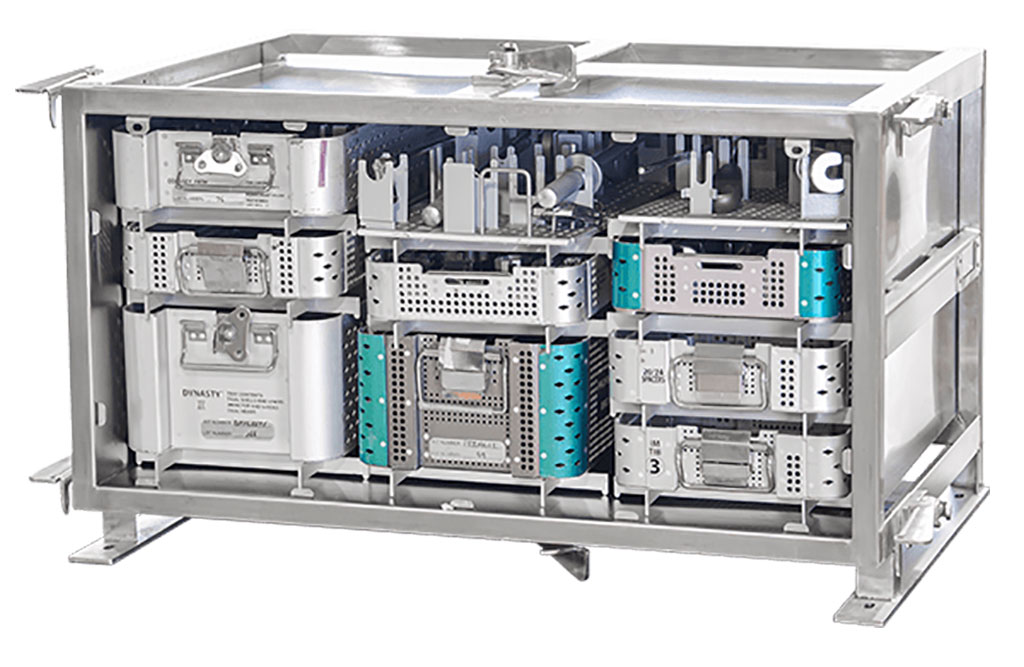
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- BD Completes Acquisition of Critical Care from Edwards Lifesciences
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Stryker Acquires care.ai to Boost AI-Driven Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Specialist V-Wave
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
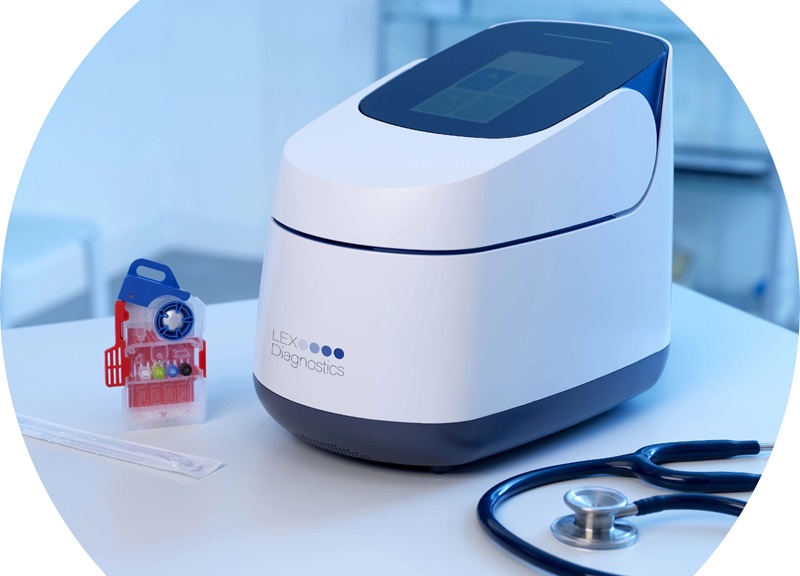
- 5-Minute Multiplex PCR Testing System to Redefine Point-Of-Care Diagnostics
- POCT for Infectious Diseases Delivers Laboratory Equivalent Pathology Results
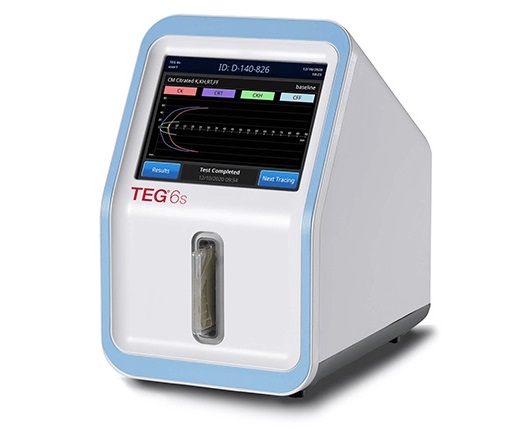
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- New Risk Scoring System Considers Role of Chronic Illness in Post-Surgery Mortality
- Implantable Cell-Based Bioelectronic Devices to Enable Patient-Specific Treatment and Disease Monitoring
- Laser-Based Headset Measures Blood Flow to Noninvasively Assess Stroke Risk
- Blocking Activity of Glucagon Hormone Could Treat Common and Challenging Type of Heart Failure
- New Tricuspid Valve Procedure Helps Patients Avoid Open-Heart Surgery
- Fast OCT System Integrated into Neurosurgical Microscope Identifies Tumor Margins During Brain Surgery
- Miniature Robots Transport Instruments for Endoscopic Microsurgery Through Body
- Robotic Visualization System for Neurosurgery Offers Greater Clarity for Complex Procedures
- Endometrial Ablation for Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Associated with High Risk of Hysterectomy
- Breakthrough Robot Technology Could Allow Entire Surgery to Be Performed Without Human Intervention
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- BD Completes Acquisition of Critical Care from Edwards Lifesciences
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Stryker Acquires care.ai to Boost AI-Driven Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Specialist V-Wave
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- 5-Minute Multiplex PCR Testing System to Redefine Point-Of-Care Diagnostics
- POCT for Infectious Diseases Delivers Laboratory Equivalent Pathology Results
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants