Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

- Edible Toothpaste-Based Transistor to Power Future Smart Pills for Monitoring Health Conditions
- Noninvasive Optical Imaging Technique Monitors Postprandial Cardiovascular Health
- AI Algorithm Automates EEG Analysis for Detecting Epilepsy with High Precision
- New Tools Take Diagnosis of Pediatric Sepsis to Next Level
- Battery-Free Device Implanted Through Minimally-Invasive Procedure Treats Bladder Leaks
- Novel Prostate Biopsy Technique Lowers Infection Risk
- Intravascular Imaging Guidance System Optimizes Stenting Procedures for Improved Patient Outcomes
- Better-Designed Operating Room Shortens Surgical Procedure Time and Produces Better Outcomes
- Spatial Computing Technology Could Revolutionize Operating Room Environment
- Innovative Catheter Guidance Technology Aims for Zero Malpositioning
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- BD Completes Acquisition of Critical Care from Edwards Lifesciences
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Stryker Acquires care.ai to Boost AI-Driven Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Specialist V-Wave
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
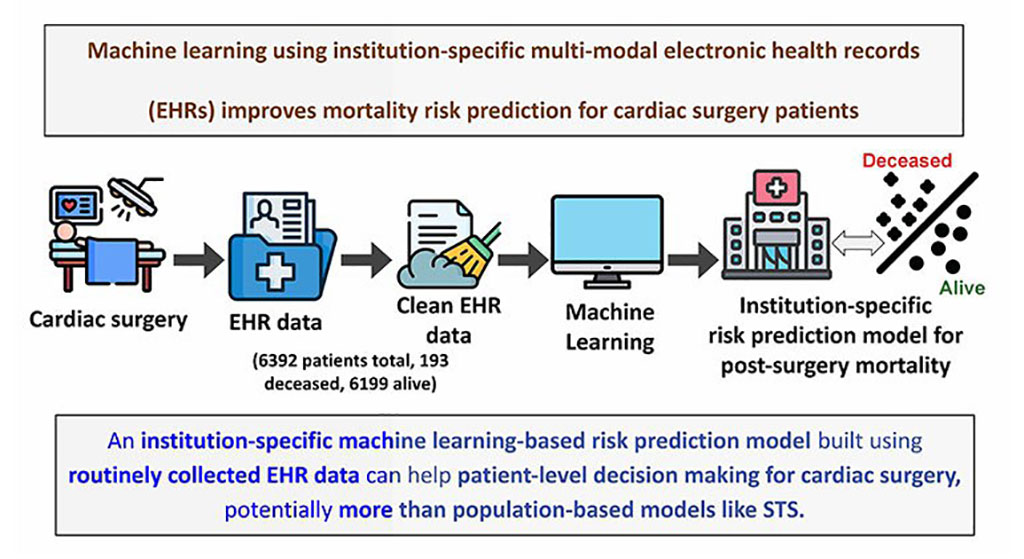
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- 5-Minute Multiplex PCR Testing System to Redefine Point-Of-Care Diagnostics
- POCT for Infectious Diseases Delivers Laboratory Equivalent Pathology Results
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- Edible Toothpaste-Based Transistor to Power Future Smart Pills for Monitoring Health Conditions
- Noninvasive Optical Imaging Technique Monitors Postprandial Cardiovascular Health
- AI Algorithm Automates EEG Analysis for Detecting Epilepsy with High Precision
- New Tools Take Diagnosis of Pediatric Sepsis to Next Level
- Battery-Free Device Implanted Through Minimally-Invasive Procedure Treats Bladder Leaks
- Novel Prostate Biopsy Technique Lowers Infection Risk
- Intravascular Imaging Guidance System Optimizes Stenting Procedures for Improved Patient Outcomes
- Better-Designed Operating Room Shortens Surgical Procedure Time and Produces Better Outcomes
- Spatial Computing Technology Could Revolutionize Operating Room Environment
- Innovative Catheter Guidance Technology Aims for Zero Malpositioning
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- BD Completes Acquisition of Critical Care from Edwards Lifesciences
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Stryker Acquires care.ai to Boost AI-Driven Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Specialist V-Wave
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- 5-Minute Multiplex PCR Testing System to Redefine Point-Of-Care Diagnostics
- POCT for Infectious Diseases Delivers Laboratory Equivalent Pathology Results
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants