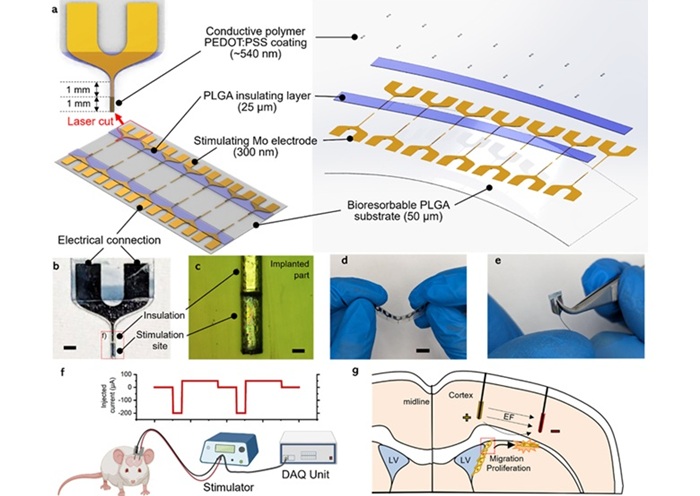
Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

- AI Model Accurately Predicts Progression of Autoimmune Disease
- AI Predicts and Identifies Subtypes of Type 2 Diabetes from Continuous Blood Glucose Monitor
- Digital Heart Twin to Help Treat Dangerous Heart Rhythms
- Miniaturized Fiber Photoacoustic Spectrometer Enables Real-Time Intravascular Blood Gas Monitoring
- Groundbreaking Dual-Functional Bone Regeneration Scaffold Shows Promise for Infected Bone Defect Treatment
- Plant Molecule Prevents Formation of Bacterial Biofilms on Catheters and Implants
- Biocompatible Sensor Implant Allows Brain Monitoring Through Development
- Biodegradable Electrodes Repair Damaged Brain Tissue Without Need for Surgical Removal
- Frugally Designed System to Improve Access to Fluorescence-Guided Surgery
- Novel Antibacterial Coating Prevents Intraoperative Bacterial Contamination in Orthopedic Implants
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- MEDICA 2024 to Highlight Hot Topics of MedTech Industry
- Start-Ups To Once Again Play Starring Role at MEDICA 2024
- Boston Scientific to Acquire AFib Ablation Company Cortex
- Hologic Acquires Gynesonics to Strengthen Existing Gynecological Surgical Business
- Smith+Nephew and JointVue Partner on Ultrasound Preoperative Planning in Robotics-Assisted Surgery
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
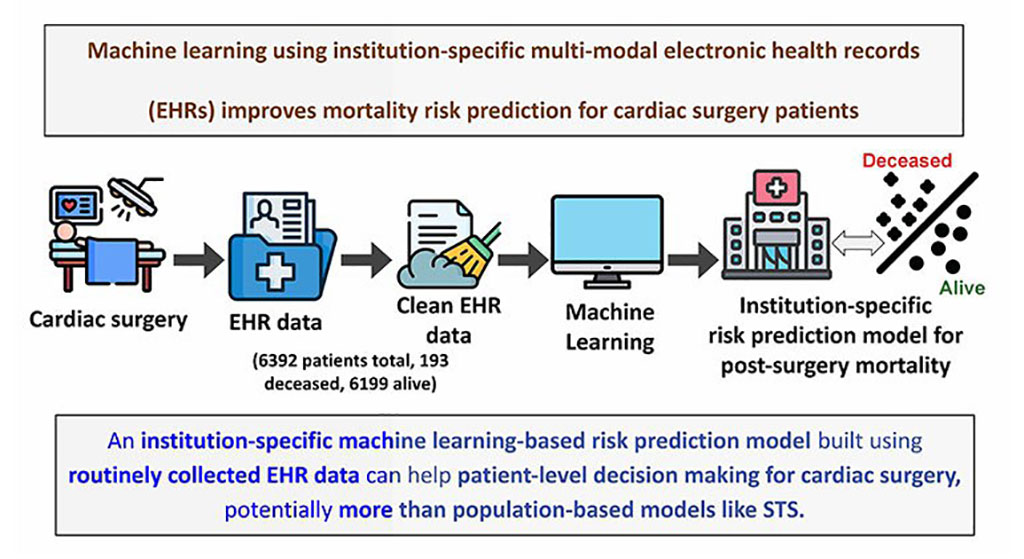
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- AI Model Accurately Predicts Progression of Autoimmune Disease
- AI Predicts and Identifies Subtypes of Type 2 Diabetes from Continuous Blood Glucose Monitor
- Digital Heart Twin to Help Treat Dangerous Heart Rhythms
- Miniaturized Fiber Photoacoustic Spectrometer Enables Real-Time Intravascular Blood Gas Monitoring
- Groundbreaking Dual-Functional Bone Regeneration Scaffold Shows Promise for Infected Bone Defect Treatment
- Plant Molecule Prevents Formation of Bacterial Biofilms on Catheters and Implants
- Biocompatible Sensor Implant Allows Brain Monitoring Through Development
- Biodegradable Electrodes Repair Damaged Brain Tissue Without Need for Surgical Removal
- Frugally Designed System to Improve Access to Fluorescence-Guided Surgery
- Novel Antibacterial Coating Prevents Intraoperative Bacterial Contamination in Orthopedic Implants
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- MEDICA 2024 to Highlight Hot Topics of MedTech Industry
- Start-Ups To Once Again Play Starring Role at MEDICA 2024
- Boston Scientific to Acquire AFib Ablation Company Cortex
- Hologic Acquires Gynesonics to Strengthen Existing Gynecological Surgical Business
- Smith+Nephew and JointVue Partner on Ultrasound Preoperative Planning in Robotics-Assisted Surgery
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds