Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

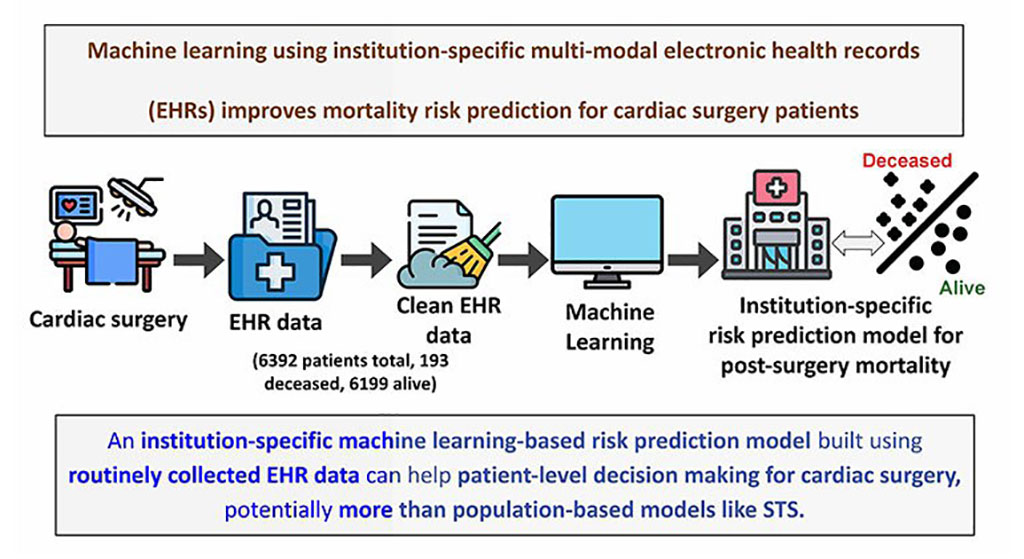
- AI Identifies Hidden Heart Valve Defects from Patient’s ECG
- Brain-Based Biomarker Could Predict Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
- AI Model Detects Hidden Diabetes Risk by Reading Glucose Spikes
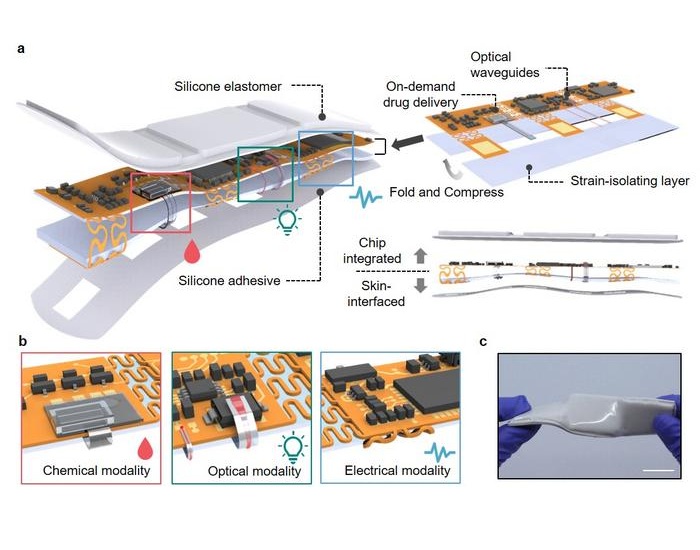
- Wearable Wound Monitoring Device to Improve Chronic Infection Care
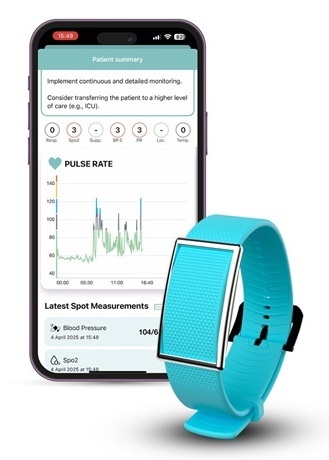
- World's First Wearable-Powered System Predicts Acute Inflammation With 90% Sensitivity
- New Endoscopy Technology Enables Early Detection of Esophageal Cancer
- New Implant Enables Women to Access Hip Resurfacing Surgery
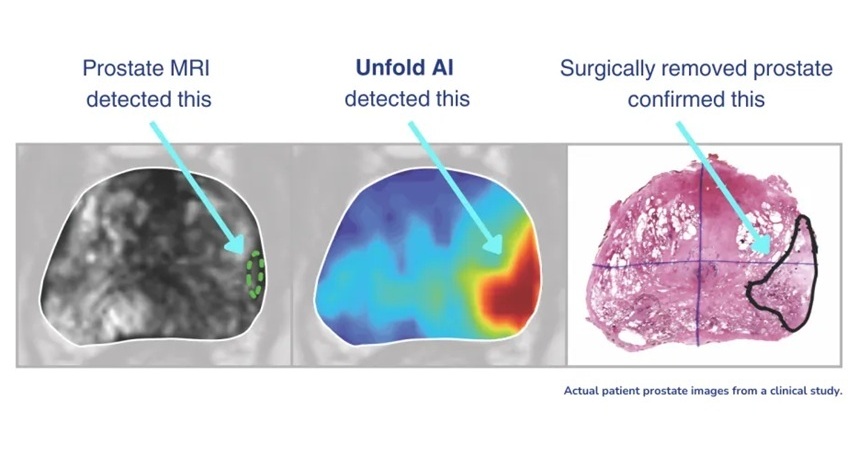
- AI Cuts Diagnostic Delays in Prostate Cancer
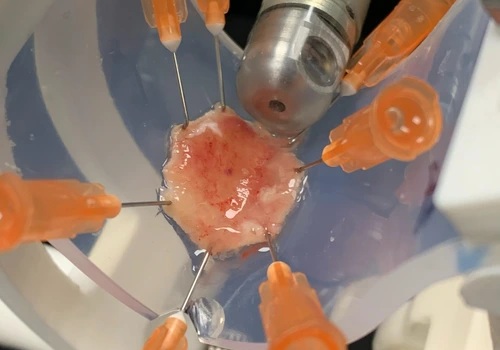
- Surgical Micro-Robot Sees and Corrects Movements from Within
- 'Google Maps' for Surgeons to Help Perform Complex Robot-Assisted Esophagectomy
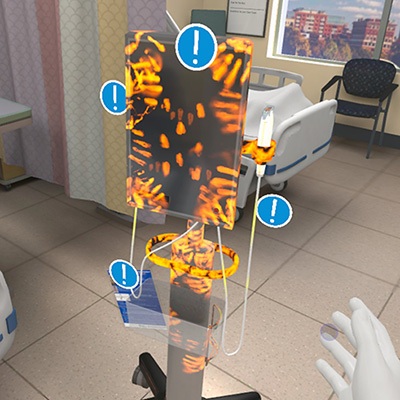
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul

 Expo
Expo
- AI Identifies Hidden Heart Valve Defects from Patient’s ECG
- Brain-Based Biomarker Could Predict Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
- AI Model Detects Hidden Diabetes Risk by Reading Glucose Spikes
- Wearable Wound Monitoring Device to Improve Chronic Infection Care
- World's First Wearable-Powered System Predicts Acute Inflammation With 90% Sensitivity
- New Endoscopy Technology Enables Early Detection of Esophageal Cancer
- New Implant Enables Women to Access Hip Resurfacing Surgery
- AI Cuts Diagnostic Delays in Prostate Cancer
- Surgical Micro-Robot Sees and Corrects Movements from Within
- 'Google Maps' for Surgeons to Help Perform Complex Robot-Assisted Esophagectomy
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul