Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

- Rapid Self-Healing Electronic Skin Paves Way for Smarter and Tougher Wearables
- Novel Needle-Free Reagent Injection Method to Reduce Spread of Infectious Diseases
- AI Model Boosts Early Delirium Detection for Improving Health Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients
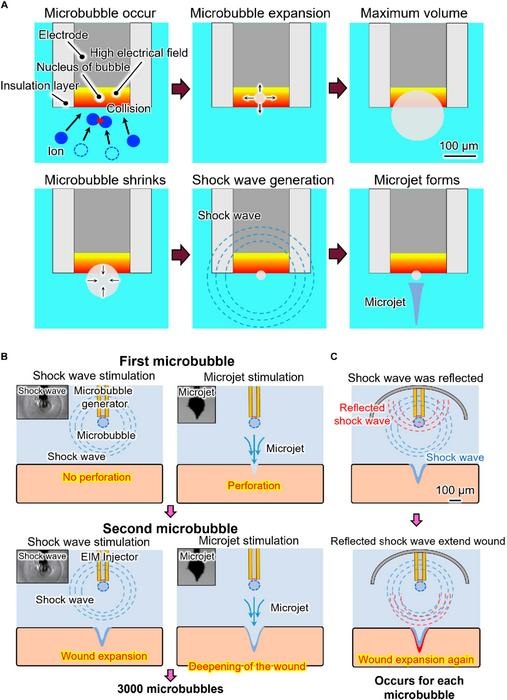
- New Ultrasound-Guided 3D Printing Technique to Help Fabricate Medical Implants
- Specialized Face Mask with Gas Sensor Detects Chronic Kidney Disease
- Ultrasound-Activated Microstructures Clean Implanted Stents and Catheters
- First-Ever MRI-Steerable Micro-Robotics to Revolutionize Glioblastoma Treatment
- Bioprinted Aortas Offer New Hope for Vascular Repair
- Early TAVR Intervention Reduces Cardiovascular Events in Asymptomatic Aortic Stenosis Patients
- New Procedure Found Safe and Effective for Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul
- Teleflex to Acquire BIOTRONIK’s Vascular Intervention Business
- Philips and Mass General Brigham Collaborate on Improving Patient Care with Live AI-Powered Insights
- Smartwatches Could Detect Congestive Heart Failure
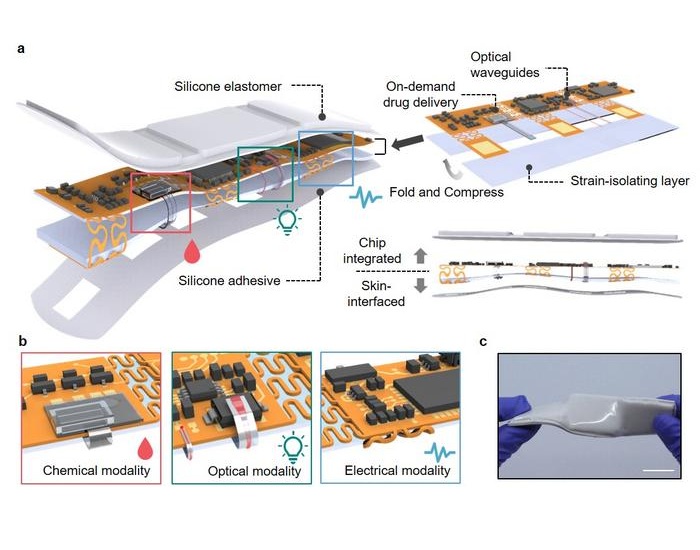
- Versatile Smart Patch Combines Health Monitoring and Drug Delivery
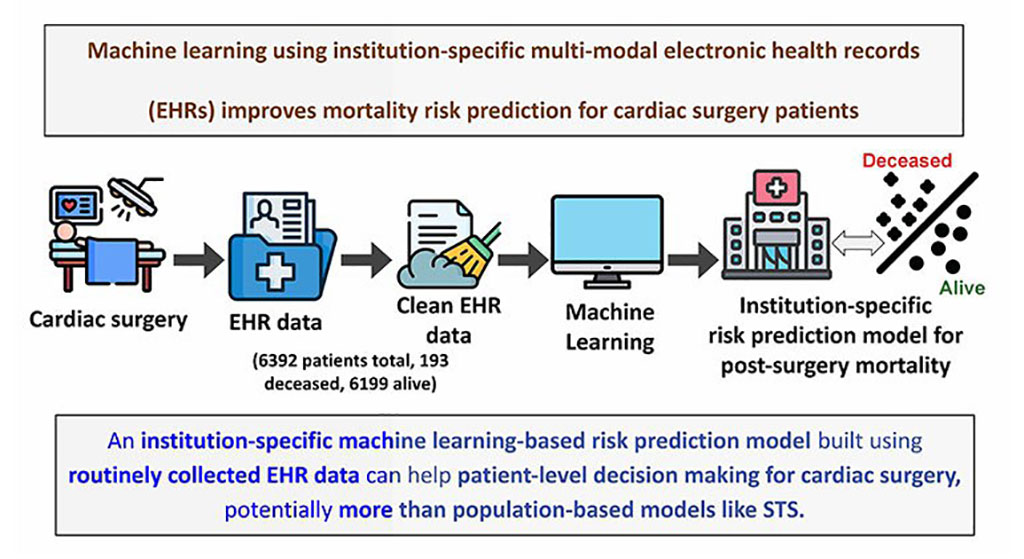
- Machine Learning Model Improves Mortality Risk Prediction for Cardiac Surgery Patients
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity

 Expo
Expo
- Rapid Self-Healing Electronic Skin Paves Way for Smarter and Tougher Wearables
- Novel Needle-Free Reagent Injection Method to Reduce Spread of Infectious Diseases
- AI Model Boosts Early Delirium Detection for Improving Health Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients
- New Ultrasound-Guided 3D Printing Technique to Help Fabricate Medical Implants
- Specialized Face Mask with Gas Sensor Detects Chronic Kidney Disease
- Ultrasound-Activated Microstructures Clean Implanted Stents and Catheters
- First-Ever MRI-Steerable Micro-Robotics to Revolutionize Glioblastoma Treatment
- Bioprinted Aortas Offer New Hope for Vascular Repair
- Early TAVR Intervention Reduces Cardiovascular Events in Asymptomatic Aortic Stenosis Patients
- New Procedure Found Safe and Effective for Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul
- Teleflex to Acquire BIOTRONIK’s Vascular Intervention Business
- Philips and Mass General Brigham Collaborate on Improving Patient Care with Live AI-Powered Insights
- Smartwatches Could Detect Congestive Heart Failure
- Versatile Smart Patch Combines Health Monitoring and Drug Delivery
- Machine Learning Model Improves Mortality Risk Prediction for Cardiac Surgery Patients
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity