Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

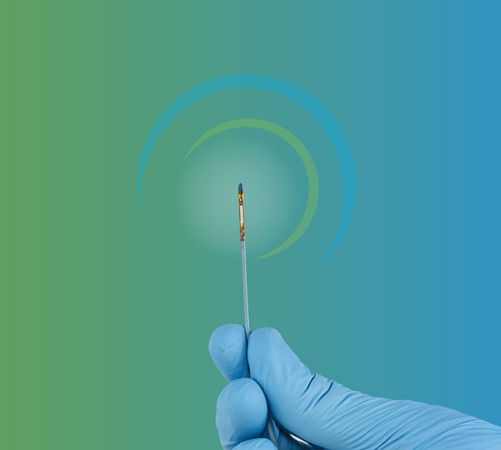
- World’s Smallest Pacemaker Fits Inside Syringe Tip
- AI-Powered, Internet-Connected Medical Devices to Revolutionize Healthcare, Finds Study
- Starfish-Inspired Wearable Tech Enables Smarter Heart Monitoring
- AI Eye Scans Could Help Identify Heart Disease and Stroke Risk
- Digital Heart Twin Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Minimally Invasive Valve Repair Reduces Hospitalizations in Severe Tricuspid Regurgitation Patients
- Tiny Robotic Tools Powered by Magnetic Fields to Enable Minimally Invasive Brain Surgery
- Magnetic Tweezers Make Robotic Surgery Safer and More Precise
- AI-Powered Surgical Planning Tool Improves Pre-Op Planning
- Novel Sensing System Restores Missing Sense of Touch in Minimally Invasive Surgery
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul
- Teleflex to Acquire BIOTRONIK’s Vascular Intervention Business
- Philips and Mass General Brigham Collaborate on Improving Patient Care with Live AI-Powered Insights
- Smartwatches Could Detect Congestive Heart Failure
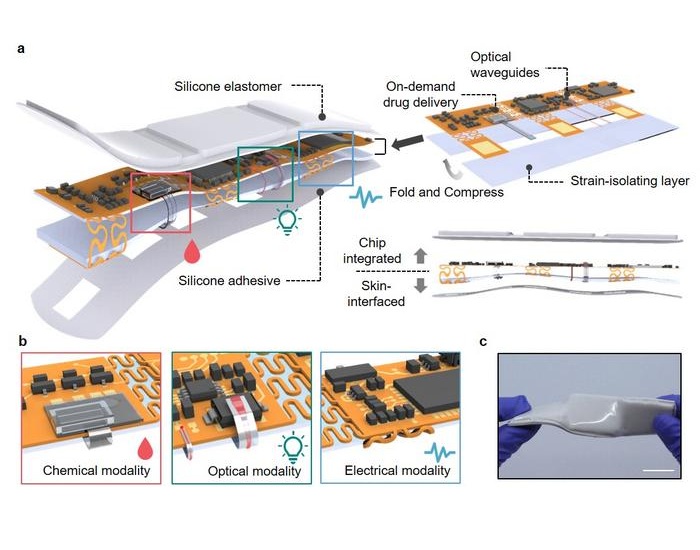
- Versatile Smart Patch Combines Health Monitoring and Drug Delivery
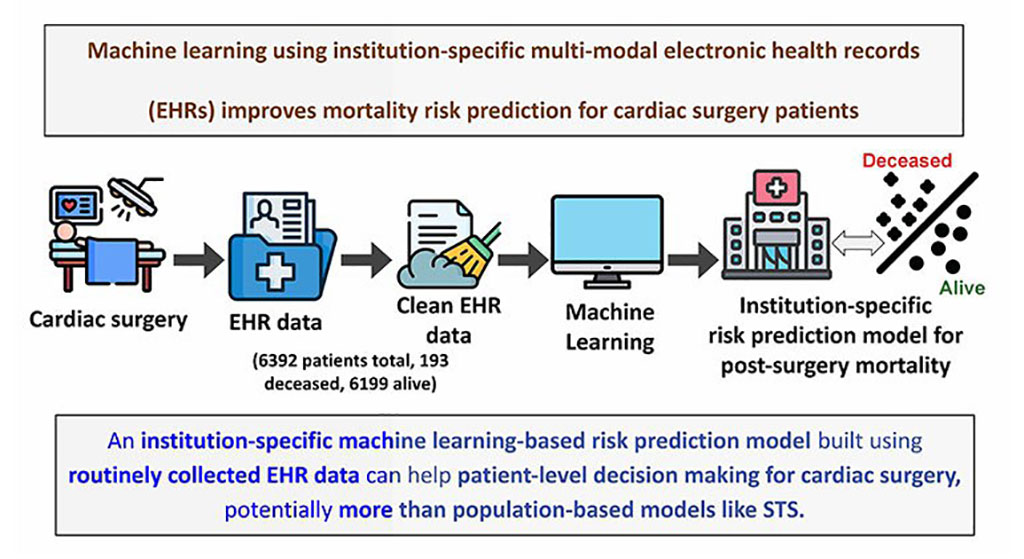
- Machine Learning Model Improves Mortality Risk Prediction for Cardiac Surgery Patients
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- World’s Smallest Pacemaker Fits Inside Syringe Tip
- AI-Powered, Internet-Connected Medical Devices to Revolutionize Healthcare, Finds Study
- Starfish-Inspired Wearable Tech Enables Smarter Heart Monitoring
- AI Eye Scans Could Help Identify Heart Disease and Stroke Risk
- Digital Heart Twin Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Minimally Invasive Valve Repair Reduces Hospitalizations in Severe Tricuspid Regurgitation Patients
- Tiny Robotic Tools Powered by Magnetic Fields to Enable Minimally Invasive Brain Surgery
- Magnetic Tweezers Make Robotic Surgery Safer and More Precise
- AI-Powered Surgical Planning Tool Improves Pre-Op Planning
- Novel Sensing System Restores Missing Sense of Touch in Minimally Invasive Surgery
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul
- Teleflex to Acquire BIOTRONIK’s Vascular Intervention Business
- Philips and Mass General Brigham Collaborate on Improving Patient Care with Live AI-Powered Insights
- Smartwatches Could Detect Congestive Heart Failure
- Versatile Smart Patch Combines Health Monitoring and Drug Delivery
- Machine Learning Model Improves Mortality Risk Prediction for Cardiac Surgery Patients
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity