Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical Techniques
Health ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

- New Autoinjector Could Transform Trauma Care in Severe Bleeding Emergencies
- CVD Risk Prediction Tool Could Guide Statin Therapy
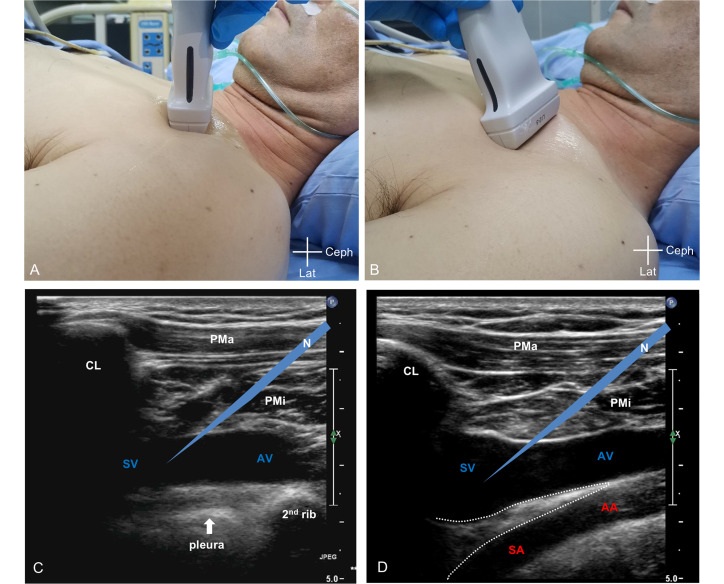
- New Ultrasound Technique Enables Safer Vein Access in Critically Ill Patient
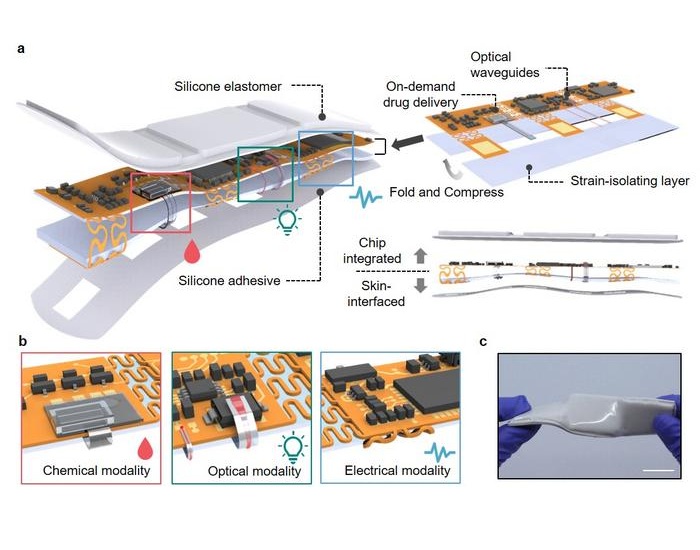
- Wearables Could Revolutionize Pregnancy Monitoring and Detect Abnormalities
- AI Model Identifies AF Patients Requiring Blood Thinners to Prevent Stroke
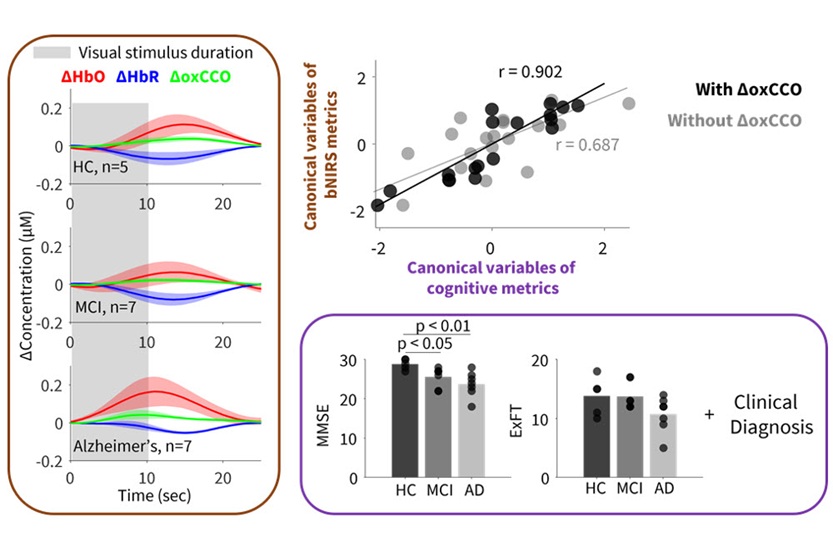
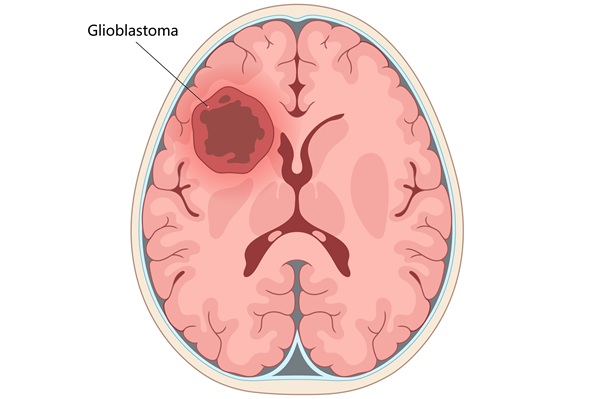
- Novel Method Uses Interstitial Fluid Flow to Predict Where Brain Tumor Can Grow Next
- World’s First Custom Anterior Cervical Spine Surgery Performed Using Personalized Implant
- Implantable Biodegradable Scaffold Helps Broken Bones Regrow Quickly
- First Human Spinal Cord Repair Using Patient Own Cells Could Cure Paralysis
- 'Dual-Mode' Tracer Enables Surgeons to See and Hear Prostate Cancer
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation

 Expo
Expo
- New Autoinjector Could Transform Trauma Care in Severe Bleeding Emergencies
- CVD Risk Prediction Tool Could Guide Statin Therapy
- New Ultrasound Technique Enables Safer Vein Access in Critically Ill Patient
- Wearables Could Revolutionize Pregnancy Monitoring and Detect Abnormalities
- AI Model Identifies AF Patients Requiring Blood Thinners to Prevent Stroke
- Novel Method Uses Interstitial Fluid Flow to Predict Where Brain Tumor Can Grow Next
- World’s First Custom Anterior Cervical Spine Surgery Performed Using Personalized Implant
- Implantable Biodegradable Scaffold Helps Broken Bones Regrow Quickly
- First Human Spinal Cord Repair Using Patient Own Cells Could Cure Paralysis
- 'Dual-Mode' Tracer Enables Surgeons to See and Hear Prostate Cancer
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation