Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

- AI-Enabled Digital Stethoscope Doubles Detection of Pregnancy Heart Failure
- Simplified Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Technique Benefits Heart Failure Patients
- Electronic Finger Wrap Uses Sweat for Automatic Monitoring of Vital Chemical Levels
- Wearable Heart Monitor Increases Diagnoses of Common Heart Rhythm Disorder By 50%
- New Chronic Coronary Syndrome Guidelines Expand Diagnostic Tools
- Sperm-Like “Micro-Robots” Navigate Through Complex Environments for Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Stent Implantation Found Preferable for Previously Untreated Non-Complex Coronary Artery Disease
- Neuroendoscopy System Improves Outcome of Minimally Invasive Neurosurgical Procedures
- AI Platform Leverages Robotic Bronchoscopy Under 3D Fluoroscopic Guidance for Precision Biopsy
- New Implant Powers Healing After Spinal Cord Injury
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Stryker Acquires care.ai to Boost AI-Driven Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Specialist V-Wave
- Abbott and Medtronic Global Partnership to Integrate Advanced Glucose Sensing Technology with Automated Insulin Delivery Systems
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
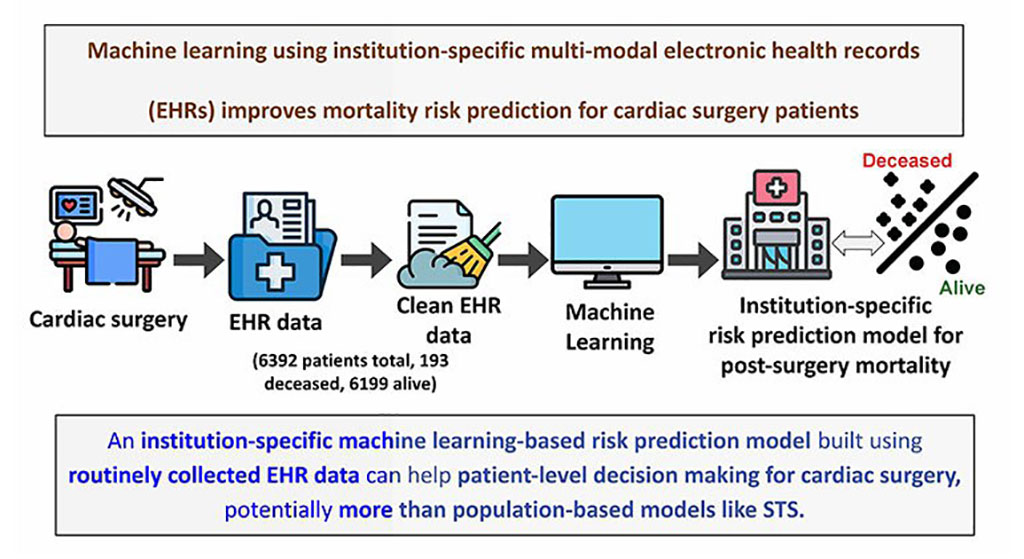
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- 5-Minute Multiplex PCR Testing System to Redefine Point-Of-Care Diagnostics
- POCT for Infectious Diseases Delivers Laboratory Equivalent Pathology Results
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- AI-Enabled Digital Stethoscope Doubles Detection of Pregnancy Heart Failure
- Simplified Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Technique Benefits Heart Failure Patients
- Electronic Finger Wrap Uses Sweat for Automatic Monitoring of Vital Chemical Levels
- Wearable Heart Monitor Increases Diagnoses of Common Heart Rhythm Disorder By 50%
- New Chronic Coronary Syndrome Guidelines Expand Diagnostic Tools
- Sperm-Like “Micro-Robots” Navigate Through Complex Environments for Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Stent Implantation Found Preferable for Previously Untreated Non-Complex Coronary Artery Disease
- Neuroendoscopy System Improves Outcome of Minimally Invasive Neurosurgical Procedures
- AI Platform Leverages Robotic Bronchoscopy Under 3D Fluoroscopic Guidance for Precision Biopsy
- New Implant Powers Healing After Spinal Cord Injury
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Stryker Acquires care.ai to Boost AI-Driven Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Specialist V-Wave
- Abbott and Medtronic Global Partnership to Integrate Advanced Glucose Sensing Technology with Automated Insulin Delivery Systems
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- 5-Minute Multiplex PCR Testing System to Redefine Point-Of-Care Diagnostics
- POCT for Infectious Diseases Delivers Laboratory Equivalent Pathology Results
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants

















.jpg)