Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

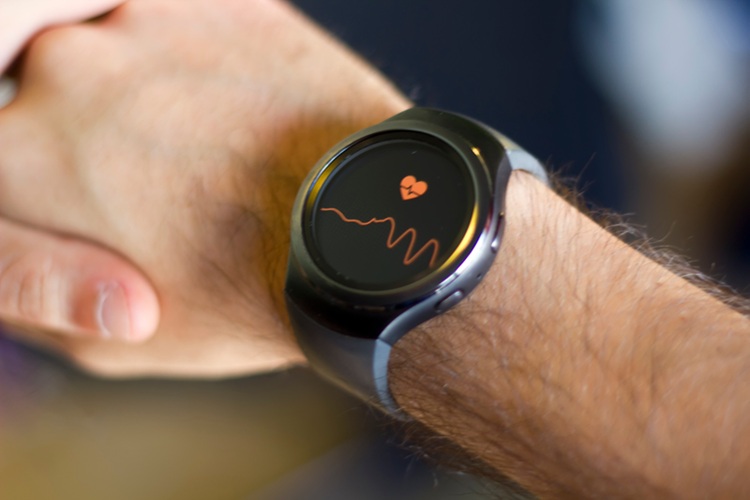
- Imaging Technology Detects Early Signs of Cardiovascular Risk Through Skin
- New Therapeutic Approach Marks Breakthrough in Pediatric Heart Disease
- AI Model Accurately Identifies Prediabetics Using Only ECG Data
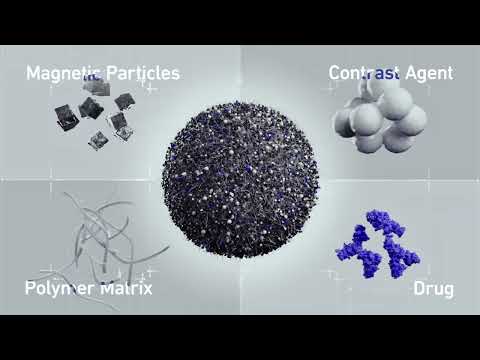
- Injectable Disease-Fighting Nanorobots to Improve Precision Cancer Therapy
- Web-Based Tool Enables Early Detection and Prevention of Chronic Kidney Disease
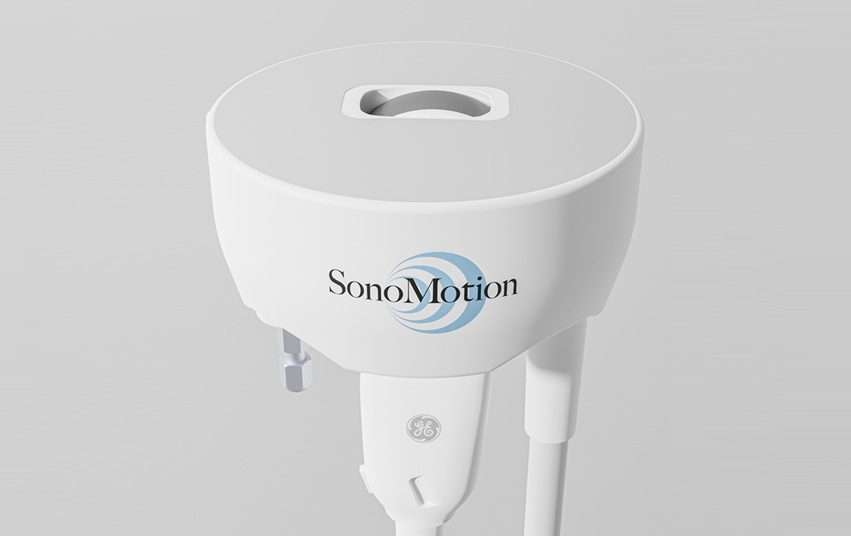
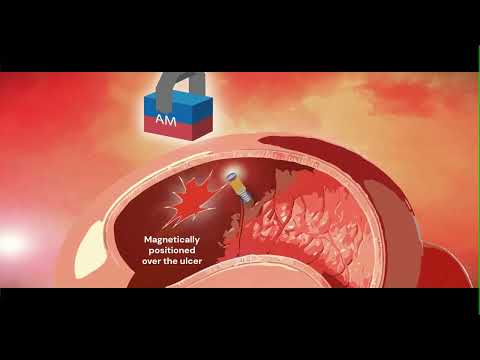
- Ultrasound Device Offers Non-Invasive Treatment for Kidney Stones
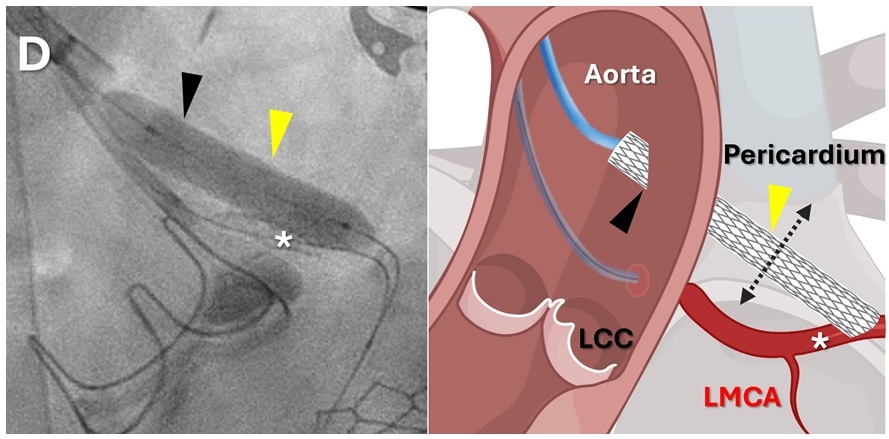
- Minimally Invasive Coronary Artery Bypass Method Offers Safer Alternative to Open-Heart Surgery
- Injectable Breast ‘Implant’ Offers Alternative to Traditional Surgeries
- AI Detects Stomach Cancer Risk from Upper Endoscopic Images
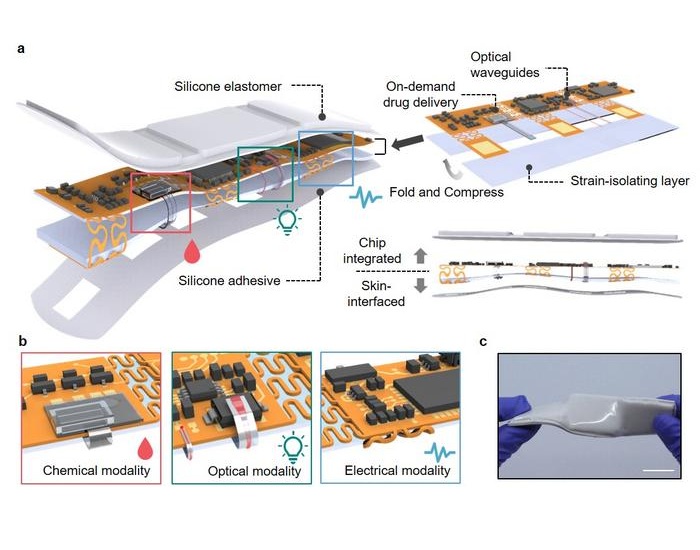
- NIR Light Enables Powering and Communicating with Implantable Medical Devices
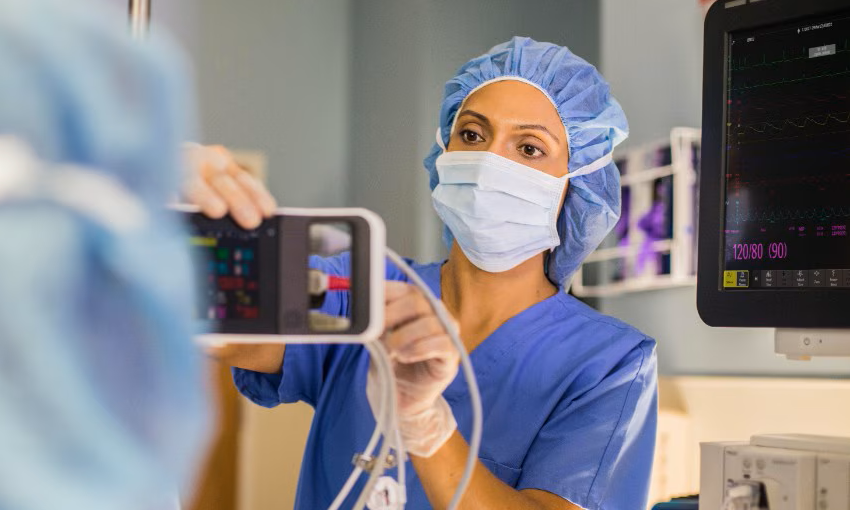
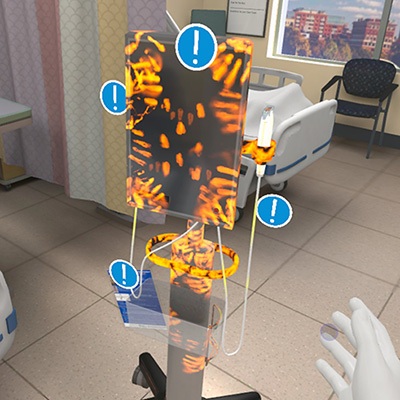
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Interoperability Push Fuels Surge in Healthcare IT Market
- Philips and Masimo Partner to Advance Patient Monitoring Measurement Technologies
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies

 Expo
Expo
- Imaging Technology Detects Early Signs of Cardiovascular Risk Through Skin
- New Therapeutic Approach Marks Breakthrough in Pediatric Heart Disease
- AI Model Accurately Identifies Prediabetics Using Only ECG Data
- Injectable Disease-Fighting Nanorobots to Improve Precision Cancer Therapy
- Web-Based Tool Enables Early Detection and Prevention of Chronic Kidney Disease
- Ultrasound Device Offers Non-Invasive Treatment for Kidney Stones
- Minimally Invasive Coronary Artery Bypass Method Offers Safer Alternative to Open-Heart Surgery
- Injectable Breast ‘Implant’ Offers Alternative to Traditional Surgeries
- AI Detects Stomach Cancer Risk from Upper Endoscopic Images
- NIR Light Enables Powering and Communicating with Implantable Medical Devices
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Interoperability Push Fuels Surge in Healthcare IT Market
- Philips and Masimo Partner to Advance Patient Monitoring Measurement Technologies
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies