Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

- AI Tool Catches Missed Illnesses Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- First Ever Device Diagnoses Life-Threatening Complication Post-Cardiac Surgery
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Use of Microbiota to Soon Become Reality
- Contactless Vital Sign Monitoring Device Measures Respiratory Rate Through Smartphones
- Dissolvable Microarray Technology Delivers Drug and Vaccine Via Patch
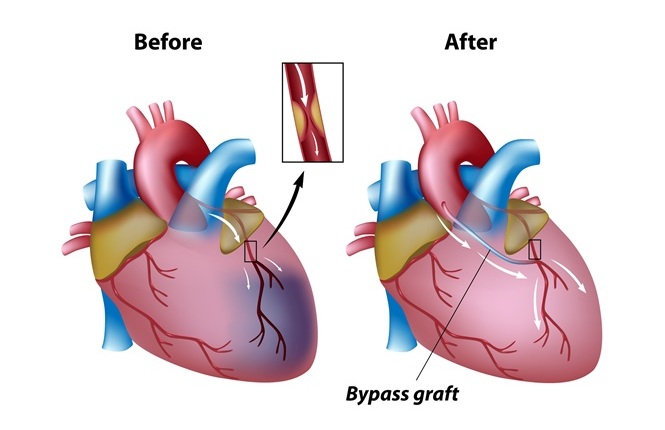
- Surgical Ablation During CABG Improves Survival in Patients with Preexisting Atrial Fibrillation
- New Battery Technology Delivers Additional Power to Implantable Medical Devices
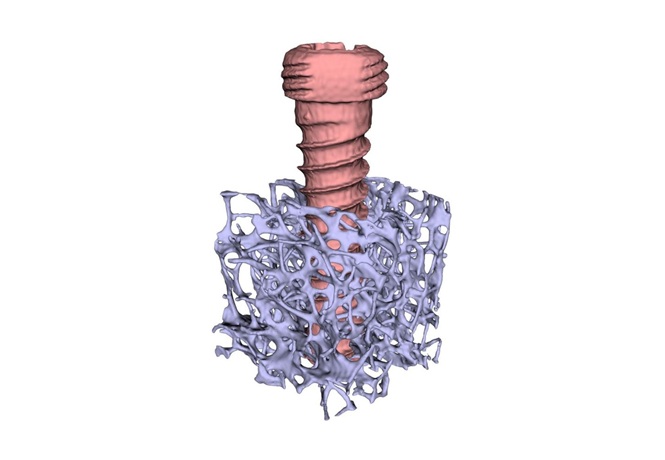
- New Model Reveals Optimal Positioning of Orthopedic Screws in Fractures
- Non-Invasive Tool for Removing Lung Cancer Tumors Reduces Surgical Trauma
- Novel Mechanical Heart Valve Improves Blood Flow and Lowers Risk of Blood Clots
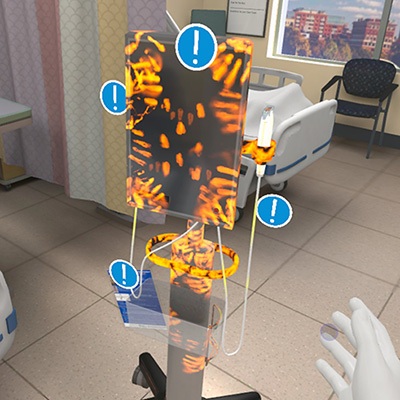
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul
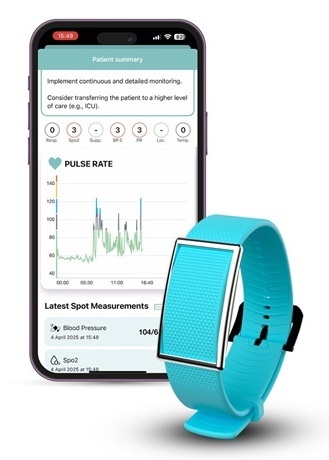
- Smartwatches Could Detect Congestive Heart Failure
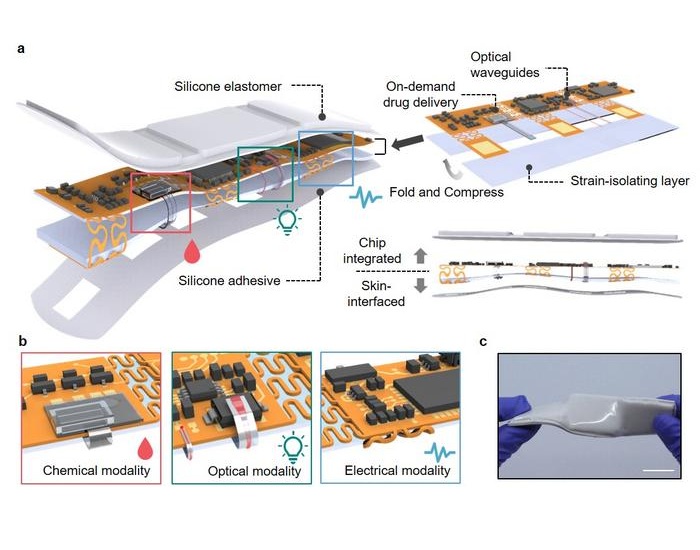
- Versatile Smart Patch Combines Health Monitoring and Drug Delivery
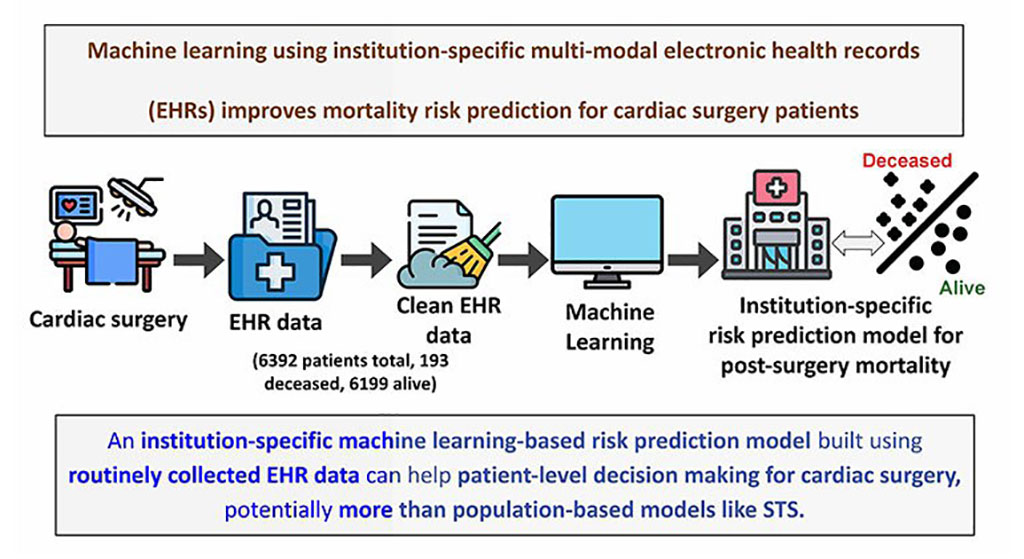
- Machine Learning Model Improves Mortality Risk Prediction for Cardiac Surgery Patients
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity

 Expo
Expo
- AI Tool Catches Missed Illnesses Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- First Ever Device Diagnoses Life-Threatening Complication Post-Cardiac Surgery
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Use of Microbiota to Soon Become Reality
- Contactless Vital Sign Monitoring Device Measures Respiratory Rate Through Smartphones
- Dissolvable Microarray Technology Delivers Drug and Vaccine Via Patch
- Surgical Ablation During CABG Improves Survival in Patients with Preexisting Atrial Fibrillation
- New Battery Technology Delivers Additional Power to Implantable Medical Devices
- New Model Reveals Optimal Positioning of Orthopedic Screws in Fractures
- Non-Invasive Tool for Removing Lung Cancer Tumors Reduces Surgical Trauma
- Novel Mechanical Heart Valve Improves Blood Flow and Lowers Risk of Blood Clots
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul
- Smartwatches Could Detect Congestive Heart Failure
- Versatile Smart Patch Combines Health Monitoring and Drug Delivery
- Machine Learning Model Improves Mortality Risk Prediction for Cardiac Surgery Patients
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity