Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

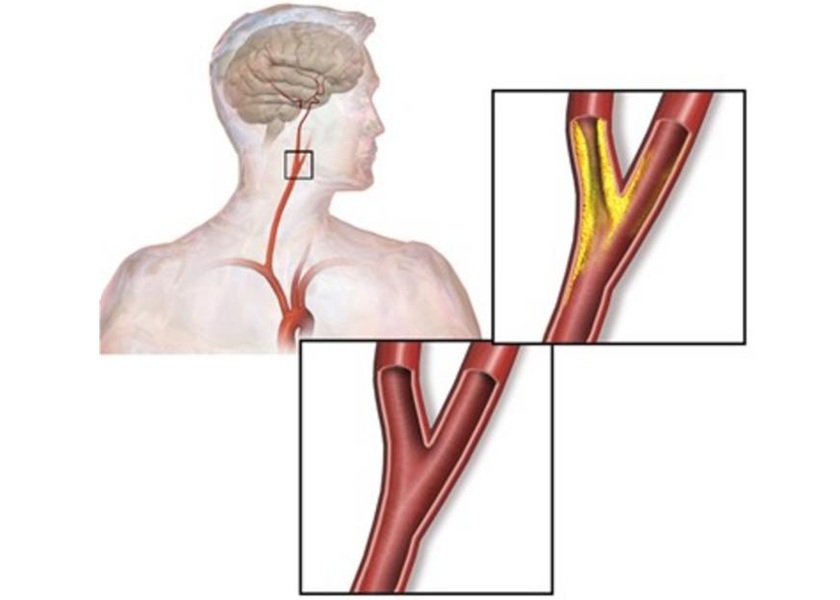
- Radioactive Microscopic Beads Could Treat Patients with Kidney Cancer
- First-Ever Medical Technology Regrows Nerves and Stops Amputations in Diabetic Patients
- AI Tool Reduces Serious Complications and Readmissions After Colorectal Cancer Surgery
- Time-Released Gel Eliminates Residual Brain Tumor Cells Post Resection
- Handheld Sensor Could Replace Blood Tests for Health Monitoring
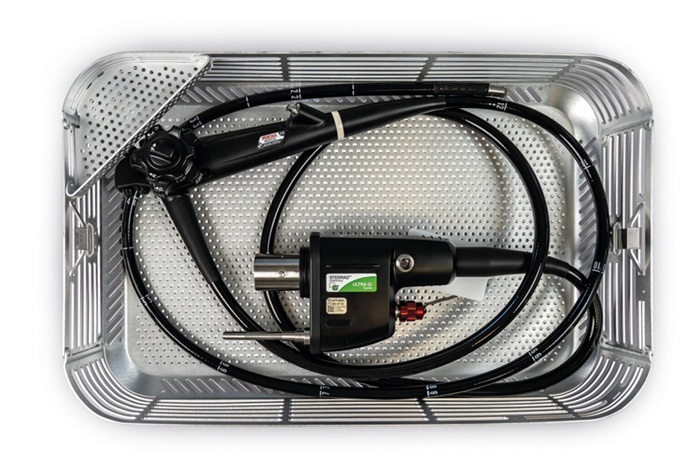
- Revolutionary Reusable Duodenoscope Introduces 68-Minute Sterilization
- World's First Transcatheter Smart Implant Monitors and Treats Congestion in Heart Failure
- Hybrid Endoscope Marks Breakthrough in Surgical Visualization
- Robot-Assisted Bronchoscope Diagnoses Tiniest and Hardest to Reach Lung Tumors
- Diamond-Titanium Device Paves Way for Smart Implants that Warn of Disease Progression
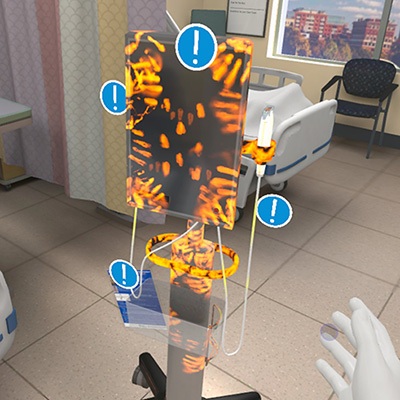
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation

 Expo
Expo
- Radioactive Microscopic Beads Could Treat Patients with Kidney Cancer
- First-Ever Medical Technology Regrows Nerves and Stops Amputations in Diabetic Patients
- AI Tool Reduces Serious Complications and Readmissions After Colorectal Cancer Surgery
- Time-Released Gel Eliminates Residual Brain Tumor Cells Post Resection
- Handheld Sensor Could Replace Blood Tests for Health Monitoring
- Revolutionary Reusable Duodenoscope Introduces 68-Minute Sterilization
- World's First Transcatheter Smart Implant Monitors and Treats Congestion in Heart Failure
- Hybrid Endoscope Marks Breakthrough in Surgical Visualization
- Robot-Assisted Bronchoscope Diagnoses Tiniest and Hardest to Reach Lung Tumors
- Diamond-Titanium Device Paves Way for Smart Implants that Warn of Disease Progression
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation