Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

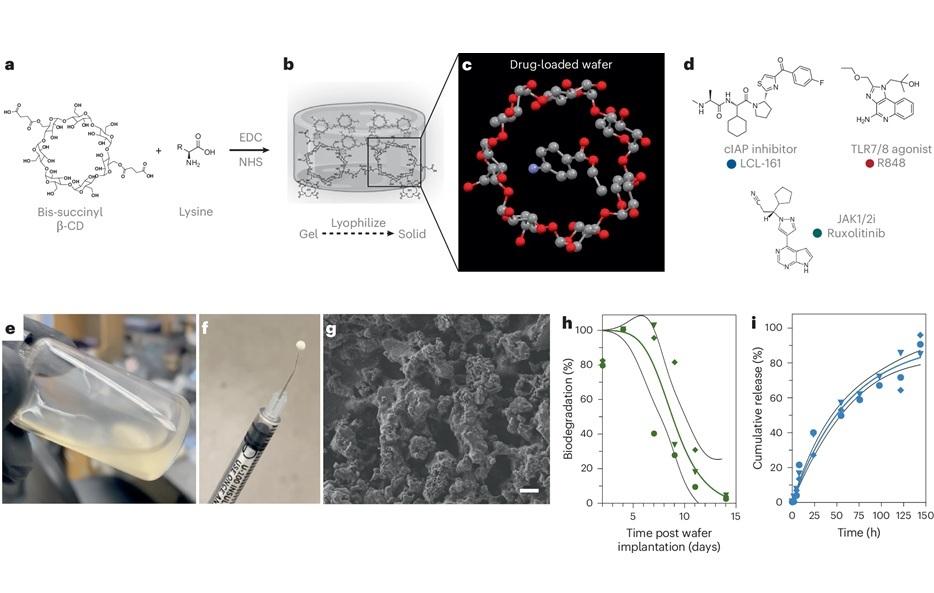
- Novel Pill Could Mimic Health Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
- AI Models Identify Patient Groups at Risk of Being Mistreated in Hospital ED
- CPR Guidelines Updated for Pediatric and Neonatal Emergency Care and Resuscitation
- Ingestible Capsule Monitors Intestinal Inflammation
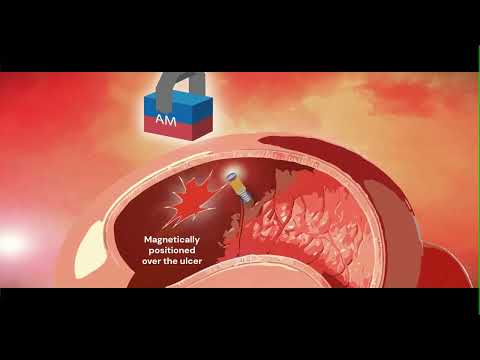
- Wireless Implantable Sensor Enables Continuous Endoleak Monitoring
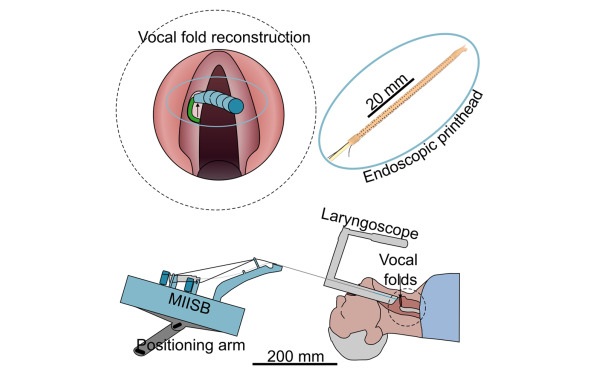
- Tiny 3D Printer Reconstructs Tissues During Vocal Cord Surgery
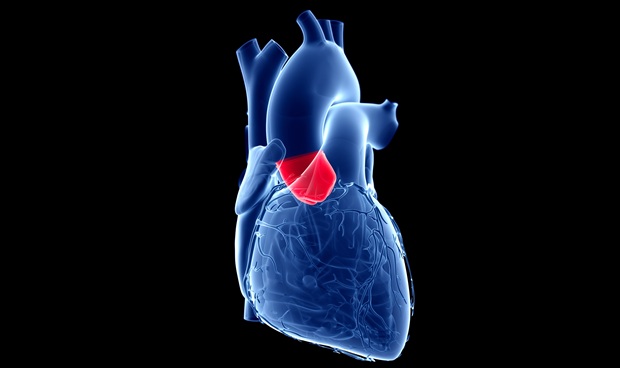
- Minimally Invasive Procedure for Aortic Valve Disease Has Similar Outcomes as Surgery
- New Nanomaterial Improves Laser Lithotripsy for Removing Kidney Stones
- Safer Hip Implant Design Prevents Early Femoral Fractures
- Ultraflexible Neurovascular Microcatheter Delivers Therapies to Tiniest Blood Vessels
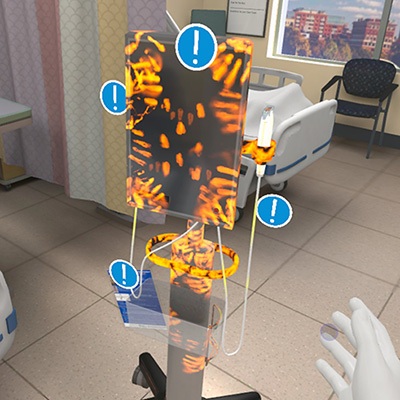
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation

 Expo
Expo
- Novel Pill Could Mimic Health Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
- AI Models Identify Patient Groups at Risk of Being Mistreated in Hospital ED
- CPR Guidelines Updated for Pediatric and Neonatal Emergency Care and Resuscitation
- Ingestible Capsule Monitors Intestinal Inflammation
- Wireless Implantable Sensor Enables Continuous Endoleak Monitoring
- Tiny 3D Printer Reconstructs Tissues During Vocal Cord Surgery
- Minimally Invasive Procedure for Aortic Valve Disease Has Similar Outcomes as Surgery
- New Nanomaterial Improves Laser Lithotripsy for Removing Kidney Stones
- Safer Hip Implant Design Prevents Early Femoral Fractures
- Ultraflexible Neurovascular Microcatheter Delivers Therapies to Tiniest Blood Vessels
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation