Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

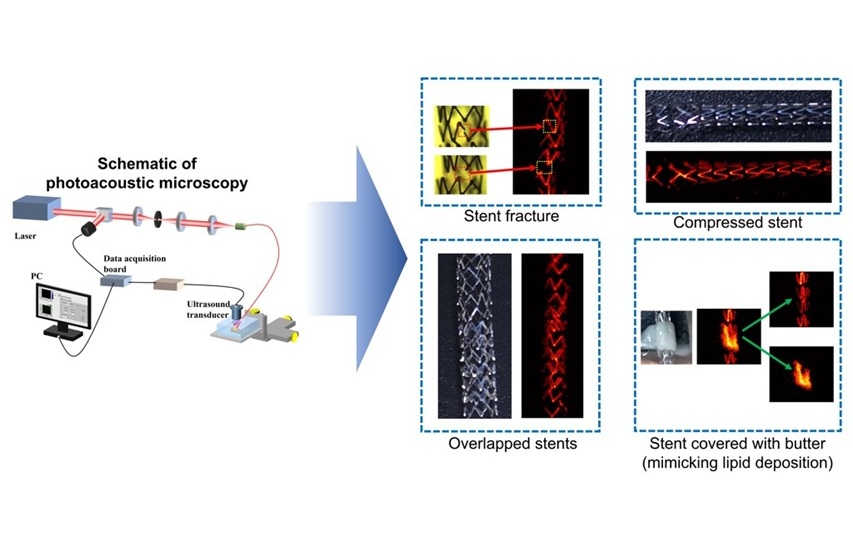
- Photoacoustic Microscopy Helps Monitor Stents Through Skin Without Surgery or Radiation
- Yogurt-Derived EV-Based Hydrogel Promotes Healing and Tissue Regeneration
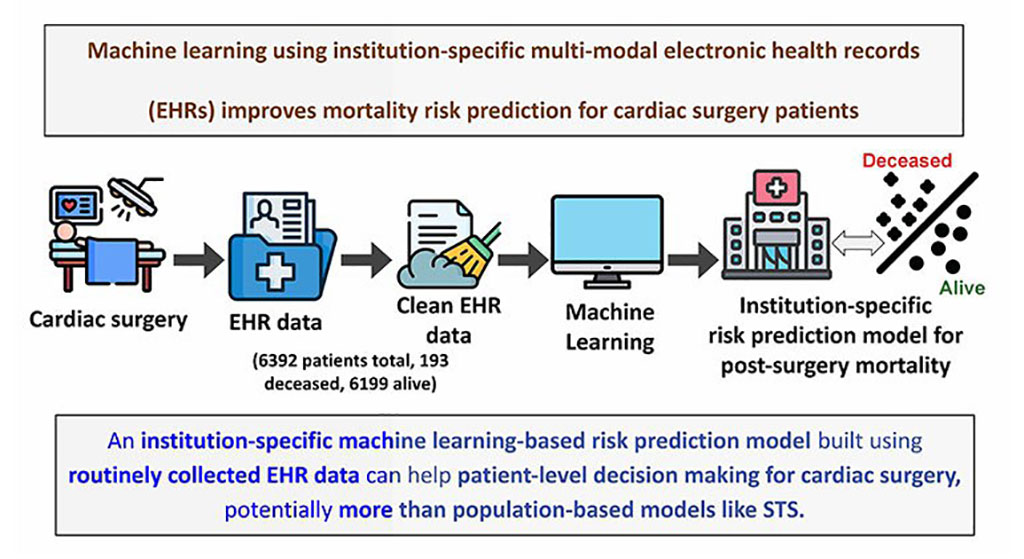
- AI Improves Prediction of Death Risk for Hospitalized Cirrhosis Patients
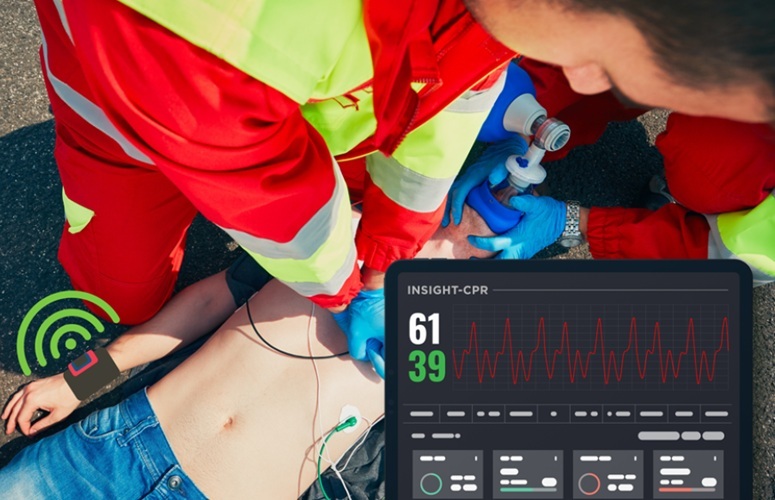
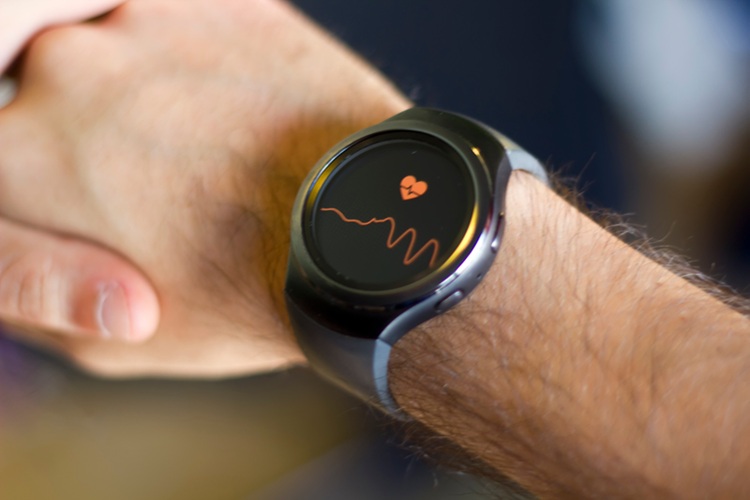
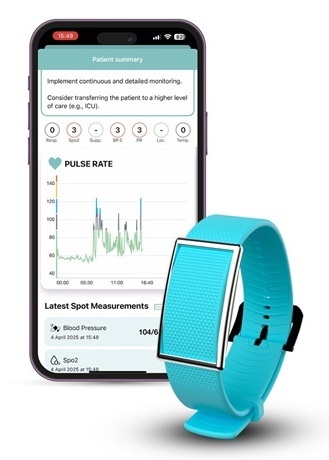
- AI-Enabled Piezoelectric Wearable to Revolutionize Joint Torque Monitoring
- New Tool Predicts Cardiovascular Disease Risk More Accurately
- New Method Could Replace Laparoscopic Surgery for Groin Hernia in Women
- Tumor-Targeting Fluorescent Bacteria Illuminate Cancer for Precision Surgery
- AI Tool Detects Surgical Site Infections from Patient-Submitted Photos
- Pioneering Technique to Increase Infant Heart Transplant by 20%
- 3D Printed Implant to Help Repair Spinal Cord Injuries
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
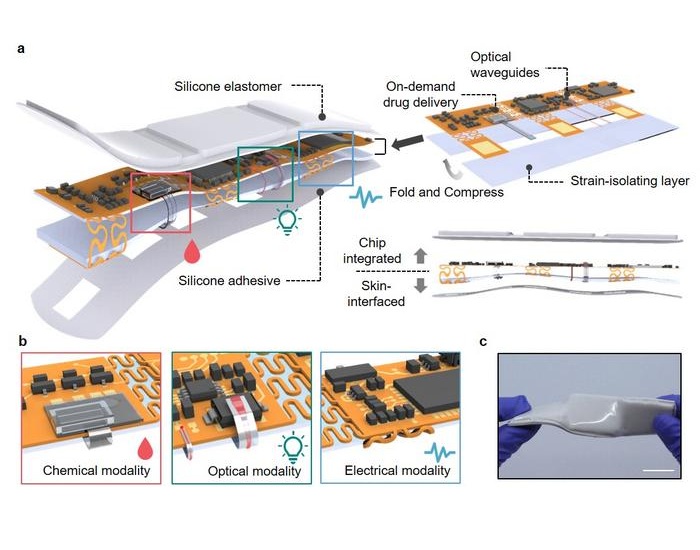
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul

 Expo
Expo
- Photoacoustic Microscopy Helps Monitor Stents Through Skin Without Surgery or Radiation
- Yogurt-Derived EV-Based Hydrogel Promotes Healing and Tissue Regeneration
- AI Improves Prediction of Death Risk for Hospitalized Cirrhosis Patients
- AI-Enabled Piezoelectric Wearable to Revolutionize Joint Torque Monitoring
- New Tool Predicts Cardiovascular Disease Risk More Accurately
- New Method Could Replace Laparoscopic Surgery for Groin Hernia in Women
- Tumor-Targeting Fluorescent Bacteria Illuminate Cancer for Precision Surgery
- AI Tool Detects Surgical Site Infections from Patient-Submitted Photos
- Pioneering Technique to Increase Infant Heart Transplant by 20%
- 3D Printed Implant to Help Repair Spinal Cord Injuries
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation
- Becton Dickinson to Spin Out Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Business
- Boston Scientific Acquires Medical Device Company SoniVie
- 2026 World Hospital Congress to be Held in Seoul