Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

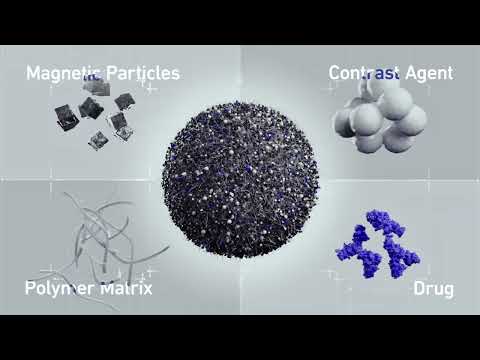
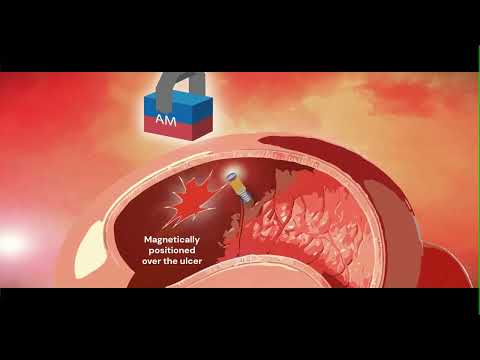
- Smart Nanomaterials Detect and Treat Traumatic Brain Injuries Simultaneously
- Earlier Blood Transfusion Could Reduce Heart Failure and Arrhythmia in Heart Disease Patients
- 'Smart' Shirt Detects Epileptic Seizures in Real Time
- Skin Patch Measures Effectiveness of Flu/COVID Vaccines in 10 Minutes
- Complete Revascularization Reduces Risk of Death from Cardiovascular Causes
- Breakthrough Surgical Device Redefines Hip Arthroscopy
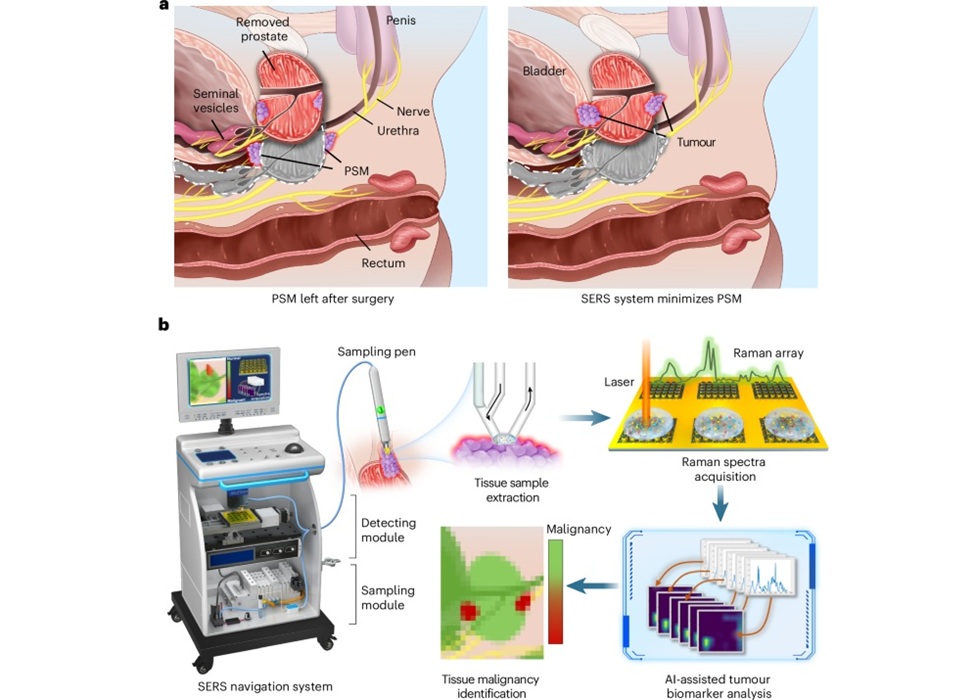
- Automated System Enables Real-Time "Molecular Pathology" During Cancer Surgery
- Groundbreaking Procedure Combines New Treatments for Liver Tumors
- Ablation Reduces Stroke Risk Associated with Atrial Fibrillation
- Optical Tracking Method Identifies Target Areas in Robot-Assisted Neurosurgery
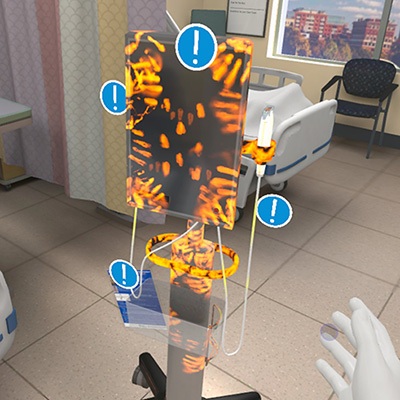
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
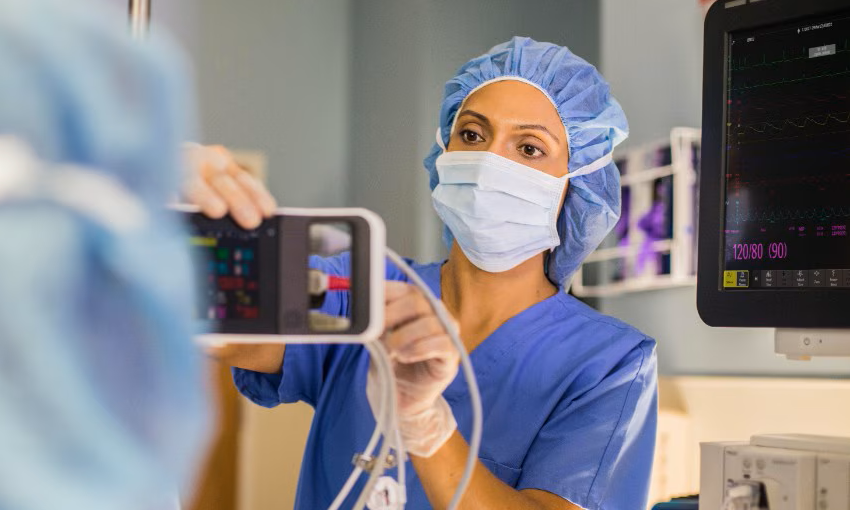
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation

 Expo
Expo
- Smart Nanomaterials Detect and Treat Traumatic Brain Injuries Simultaneously
- Earlier Blood Transfusion Could Reduce Heart Failure and Arrhythmia in Heart Disease Patients
- 'Smart' Shirt Detects Epileptic Seizures in Real Time
- Skin Patch Measures Effectiveness of Flu/COVID Vaccines in 10 Minutes
- Complete Revascularization Reduces Risk of Death from Cardiovascular Causes
- Breakthrough Surgical Device Redefines Hip Arthroscopy
- Automated System Enables Real-Time "Molecular Pathology" During Cancer Surgery
- Groundbreaking Procedure Combines New Treatments for Liver Tumors
- Ablation Reduces Stroke Risk Associated with Atrial Fibrillation
- Optical Tracking Method Identifies Target Areas in Robot-Assisted Neurosurgery
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation