Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

- Peptide-Based Hydrogels Repair Damaged Organs and Tissues On-The-Spot
- One-Hour Endoscopic Procedure Could Eliminate Need for Insulin for Type 2 Diabetes
- AI Can Prioritize Emergency Department Patients Requiring Urgent Treatment
- AI to Improve Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation
- Stretchable Microneedles to Help In Accurate Tracking of Abnormalities and Identifying Rapid Treatment
- Tiny Robots Made Out Of Carbon Could Conduct Colonoscopy, Pelvic Exam or Blood Test
- Miniaturized Ultrasonic Scalpel Enables Faster and Safer Robotic-Assisted Surgery
- AI Assisted Reading Tool for Small Bowel Video Capsule Endoscopy Detects More Lesions
- First-Ever Contact Force Pulsed Field Ablation System to Transform Treatment of Ventricular Arrhythmias
- Caterpillar Robot with Built-In Steering System Crawls Easily Through Loops and Bends
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- Mindray to Acquire Chinese Medical Device Company APT Medical
- Olympus Acquires Korean GI Stent Maker Taewoong Medical
- Karl Storz Acquires British AI Specialist Innersight Labs
- Stryker to Acquire French Joint Replacement Company SERF SAS
- Medical Illumination Acquires Surgical Lighting Specialist Isolux
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
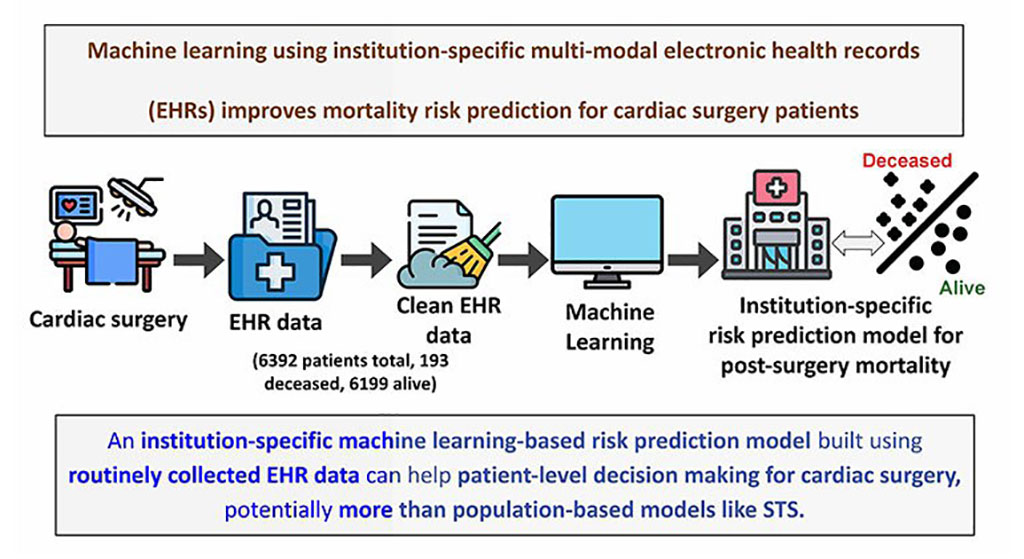
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use
- Unique Quantitative Diagnostic System Enables Immediate Diagnosis and Treatment at POC
- POC Myocardial Infarction Test Delivers Results in 17 Minutes

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- Peptide-Based Hydrogels Repair Damaged Organs and Tissues On-The-Spot
- One-Hour Endoscopic Procedure Could Eliminate Need for Insulin for Type 2 Diabetes
- AI Can Prioritize Emergency Department Patients Requiring Urgent Treatment
- AI to Improve Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation
- Stretchable Microneedles to Help In Accurate Tracking of Abnormalities and Identifying Rapid Treatment
- Tiny Robots Made Out Of Carbon Could Conduct Colonoscopy, Pelvic Exam or Blood Test
- Miniaturized Ultrasonic Scalpel Enables Faster and Safer Robotic-Assisted Surgery
- AI Assisted Reading Tool for Small Bowel Video Capsule Endoscopy Detects More Lesions
- First-Ever Contact Force Pulsed Field Ablation System to Transform Treatment of Ventricular Arrhythmias
- Caterpillar Robot with Built-In Steering System Crawls Easily Through Loops and Bends
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- Mindray to Acquire Chinese Medical Device Company APT Medical
- Olympus Acquires Korean GI Stent Maker Taewoong Medical
- Karl Storz Acquires British AI Specialist Innersight Labs
- Stryker to Acquire French Joint Replacement Company SERF SAS
- Medical Illumination Acquires Surgical Lighting Specialist Isolux
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use
- Unique Quantitative Diagnostic System Enables Immediate Diagnosis and Treatment at POC
- POC Myocardial Infarction Test Delivers Results in 17 Minutes